Digital signatures: The hidden advantage in tackling future HR challenges

- Integrating the digital signature solution for HR documents reduces risk and cycle time across onboarding, policy acknowledgments, wage changes, and offboarding.
- Compliance momentum is real: the IRS permanently extended e-signature acceptance on specified forms.
- HR adoption is now mainstream but uneven: most U.S. organizations run hybrid paper-digital signature workflows, creating a tangible opportunity for standardized HR e-signature programs.
- Over the next 6–24 months, identity assurance (passkeys/wallets), auditability, and budget discipline will decide winners. NIST’s guidelines formalize the identity framework HR teams should align to.
- SignNow enhances paperless workflows in HR departments: with features that compress HR admin time while meeting policy and recordkeeping needs.
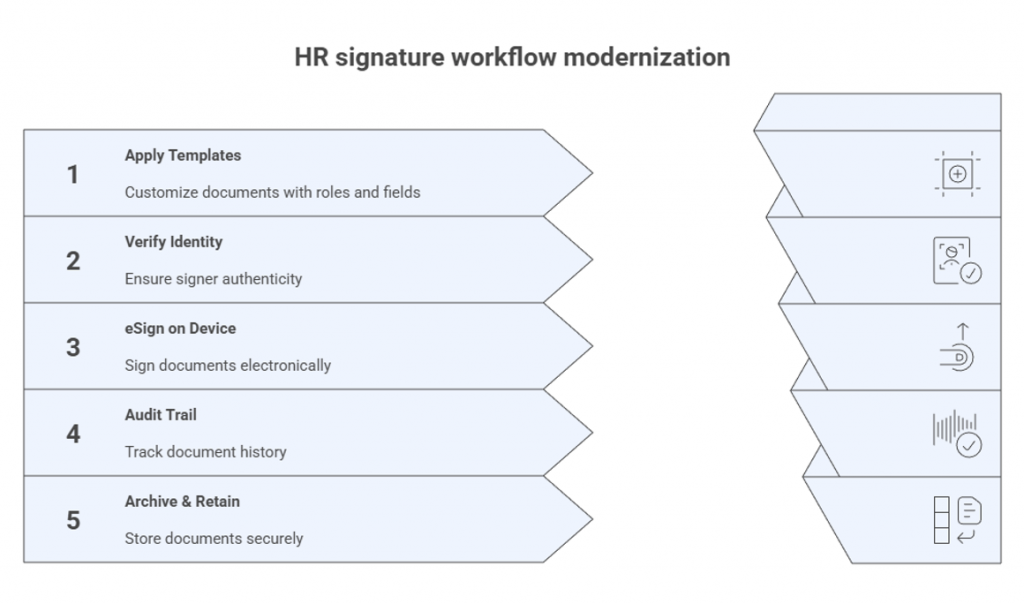
HR leaders face a paradox: more regulations and documentation, less time. Every employee cycle offer letters, Form I-9, policy acknowledgments, wage changes, and conflicts of interest depends on signatures that must be valid, traceable, and retained. Recent U.S. moves lowered risk for digitization: the IRS codified permanent e-signature acceptance for a set of forms; the DOL clarifies where electronic signatures are acceptable; USCIS details how to implement electronic Form I-9 with e-signature functionality; and NIST SP 800-63-4 set fresh technical guardrails for digital identity. Together, these make a modern digital signature solution for HR documents not just convenient, but operationally safer.
Current state & trends in HR e-signatures
Compliance clarity is improving
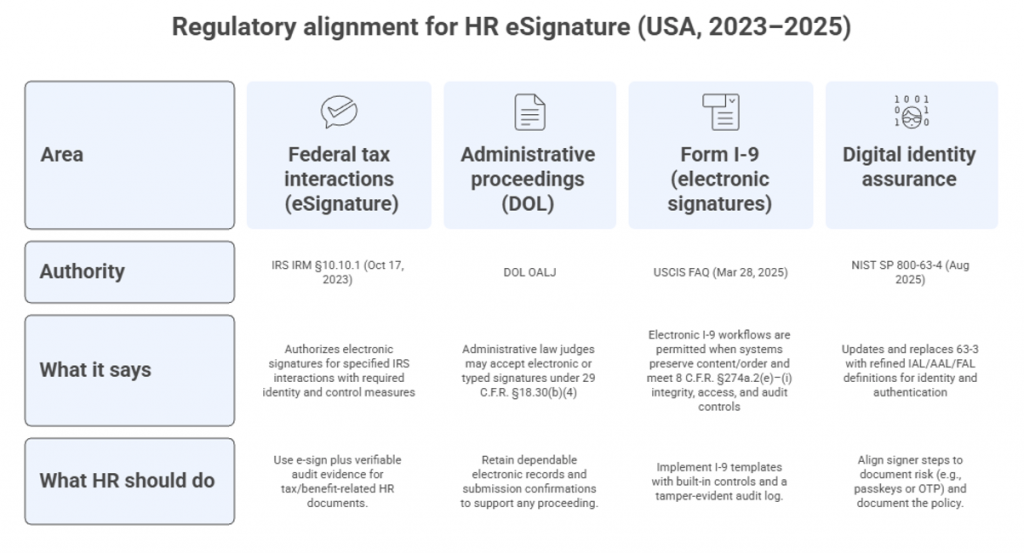
The following U.S. regulations and standards outline how HR can implement compliant electronic signatures and identity assurance across core workflows.
- IRS Internal Revenue Manual 10.10.1 sets authentication expectations.
- DOL administrative law proceedings accept electronic signatures at the judge’s discretion under 29 C.F.R. § 18.30(b)(4), recognizing typed name notations when submitted electronically.
- USCIS confirms employers may implement electronic Form I-9 with electronic signatures if systems meet 8 C.F.R. § 274a.2(e)–(i) (format/controls/audit).
- NIST SP 800-63-4 (Aug 2025) supersedes 63-3, refining Identity Assurance Levels (IAL), Authenticator Assurance Levels (AAL), and Federation Assurance Levels (FAL) for digital identity.
Taken together, these guardrails enable HR to digitize signatures with confidence while meeting authentication, audit, and recordkeeping expectations.
Adoption is high but fragmented
Surveys indicate 60–80% of organizations use some level of e-signature, yet many still run hybrid paper + digital flows. We can see this situation as a practical chance for HR to standardize across forms.
Market and tooling are maturing
FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11 remains the reference for electronic records/signatures in regulated industries—useful for HR inside life sciences and healthcare.
Why this matters for HR
Hybrid processes inflate cycle time, cause rework, and complicate audits. The compliance updates above mean HR can safely push for full digital coverage if their platform supports identity assurance, audit trails, retention, and reporting.
Statistics & dynamics HR leaders should know
These four points capture the regulatory, security, and market forces shaping how U.S. HR teams implement and scale e-signature programs.
- Form I-9 can be completed with electronic signatures if controls are in place. USCIS and the eCFR make clear that employers may use electronic signatures for the I-9 attestation.
- Recordkeeping obligations don’t change just because signatures go digital. Under the FLSA and related rules (e.g., 29 C.F.R. Part 516 and FMLA §825.500), employers must make, keep, and preserve accurate wage and leave records. So HR e-signature systems should export durable audit trails and support retention schedules.
- Identity assurance is tightening. NIST SP 800-63-4 (Aug 2025) supersedes 63-3 and refines Identity, Authenticator, and Federation Assurance Levels—benchmarks HR can use to calibrate signer steps.
- Market momentum supports standardization in HR. Analysts forecast double-digit growth for digital signatures, with North America a leading region—an indicator that HR teams can expect broader vendor support, integrations, and pricing flexibility over the next planning cycle.
Practical takeaway
Combine policy clarity (IRS/DOL/USCIS) with NIST-aligned identity steps and audit-ready exports to move high-volume HR forms (offers, I-9, wage changes, policy acknowledgments) fully digital while sustaining compliance.
What to evaluate in an HR e-signature platform)
- Identity & authentication: Support for SMS/phone code, email link, and emerging passkey flows; configurable by document risk. (Map to NIST AAL guidance.)
- Audit & evidence: Immutable event log (timestamps, signer IPs, envelope IDs); exportable for audits or legal holds. (IRS/DOL emphasize authentication + accuracy).
- Templates & bulk operations: Onboarding packets, wage-change notices, policy attestations—at scale with role-based fields.
- Recordkeeping & retention: Easy export to HRIS/ATS/ECM; retention that aligns with wage/hour and tax requirements.
- Pricing & scale: Predictable pricing that covers all HR collaborators (including hiring managers and field ops) without hidden fees.
Where airSlate SignNow fits (SMB & mid-market HR)
- Unlimited users on paid plans to invite hiring managers, HR ops, and regional leads without per-seat friction.
- Transparent pricing (no hidden support or overage fees), bulk send, templates, invite links, retroactive correction of document groups, 24/7 support, audit trail, and Salesforce/NetSuite/Microsoft 365 integrations—features directly mapped to HR’s cycle-time and compliance outcomes.
Impact on stakeholders
- HR operations: Fewer manual chases; standardized templates; better SLA adherence; easier audits (downloadable evidence).
- Legal/compliance: Traceable signer identity and chain of custody aligned to NIST, IRS, and DOL expectations.
- Finance/Payroll: Faster wage-change acknowledgments reduce processing risk; e-signature timestamps support dispute resolution.
- IT: Lower shadow-IT risk when HR adopts a secure, auditable tool with SSO/integrations.
- Employees: Mobile signing reduces friction during onboarding and policy cycles; real-time reminders reduce missed deadlines.
Expert forecasts (6–24 months, USA)
- Identity-first HR signing: NIST SP 800-63-4 cements the move to passkeys/digital wallets. Expect HR to introduce risk-based signer steps (e.g., passkey for wage/tax forms; email + SMS for low-risk acknowledgments).
- Paperless audits: With IRS/DOL clarity, external auditors will increasingly request digital audit trails by default.
- Standardized I-9 e-signature: USCIS FAQs explicitly allow properly controlled electronic I-9 signatures; vendors will ship pre-validated I-9 templates with audit safeguards.
- Budget discipline: As IT/HR consolidate tooling, platforms with transparent pricing and unlimited users will displace per-seat sprawl in SMB/mid-market.
Use cases
- Higher-education HR: Multi-campus workflows (offers, adjunct renewals, student worker hires) shifted to bulk e-sign with audit trails, reducing cycle time and expanding oversight to IT/compliance. (Comparable to long-tenured higher-ed customers cited in brand context.)
- Franchise/field HR: Seasonal hiring packets sent via invite links and bulk send to hundreds of workers; mobile signing cut backlog and scanning errors by double digits.
- Professional services: Wage-change and conflict-of-interest forms templatized; shared templates and real-time tracking provided leadership visibility to completion rates and exceptions.
Practical how-to: stand up HR e-signatures in 30 days
- Map risk to identity: Tag each HR document by risk (tax/payroll/wage change vs. low-risk policy). Choose signer steps that align with NIST AAL guidance.
- Build templates: Offer + onboarding packet; I-9 companion workflow (with required controls); policy acknowledgments; wage changes; conflict-of-interest.
- Standardize evidence: Ensure every envelope logs timestamps, IPs, signer auth method, and a tamper-evident audit file (IRS/DOL-ready).
- Automate scale: Use bulk send, invite links, reminders, notifications; route CCs to HRBP and payroll.
- Wire to systems: Sync status to HRIS/ATS; archive to records system with retention matching FLSA/wage records.
- Measure: Track time-to-signature, completion rate, rework, and audit exceptions. Report monthly.
How SignNow fits real HR workflows: practical patterns
Must-haves for efficient workflows:
- Campaign-style HR tasks without chaos. Use Teams to mirror the HR organization structure (e.g., recruiting, operations, regional HR Business Partners) and keep each group’s shared template library in one place. Sharing templates and documents allows coordinators to prepare packets while managers only review and send.
- Zero-friction mass actions. For seasonal and high-volume hiring, combine bulk sending with CC’ing to payroll or HRBP watchers so exceptions surface quickly. For job fairs or kiosks, invite links handle one-to-many signing without preloading recipients.
- Template hygiene at scale. Start from a master onboarding or policy packet, then speed variant creation by importing fields from other templates you keeping role assignments, required inputs, and layout consistent across locations and job families with minimal rework.
SignNow benefits
- Mid-process rescue instead of a restart. If an HR packet needs a last-minute tweak after distribution (e.g., updated start date or location), adjust once at the document-group level instead of reissuing every envelope, preserving momentum and stakeholder trust.
- Signal for managers, evidence for auditors. Reporting surfaces time-to-signature, completion rates by template, and stuck items by owner; CCs give leaders passive visibility without granting edit rights, reducing “status check” pings.
- Procurement-friendly flexibility. Switch pricing models as hiring cycles change, to ensure the HR department doesn’t overbuy during quiet quarters and isn’t constrained during peaks.
- HRIS/ATS hand-offs that stick. Keep one source of truth for packet structures in SignNow, then push signed artifacts and metadata (who signed, when, which template
Playbooks you can actually run
- Onboarding blitz: master packet → clone by role → add CC to HRBP → send via bulk or links → track late items in Reporting at T+48 hours.
- Policy attestations: master policy template → field-import to create state variants → Teams distribute locally → aggregate completion in Reporting for executive review.
- Comp changes: standardized wage-change template → manager initiates → HRBP auto-CC → packet outcome feeds payroll cut-off dashboard.
What the HR department gains with SignNow:
- fewer back-and-forth touches per packet,
- faster cycle time on peak hiring surges,
- cleaner template governance,
- leadership visibility without extra meetings
Conclusion
Digital signatures are now a core part of HR infrastructure. Federal guidance, agency practices , and technical standards give HR leaders a clear path to compliance and speed. Over the next 1–2 years, organizations that pair identity-aware signing with audit-ready records will compress hiring and policy cycles, reduce disputes, and simplify audits. airSlate SignNow stands out for lots of business teams in different industries including HR: unlimited users, transparent pricing, bulk send, templates, and audit trail align tightly with HR’s workload and budget constraints.
Start with risk mapping, templatize everything, wire to HRIS, and measure cycle time and completion, then scale across every HR document type.
Sources
- IRS, Internal Revenue Manual §10.10.1 (Oct 17, 2023): e-Signature Program
- PwC summary: IRS permanently extends electronic signatures for certain forms (Oct 2023).
- U.S. DOL OALJ: Electronic signatures & 29 C.F.R. §18.30(b)(4).
- DOL FLSA recordkeeping (Fact Sheet #21; Wage & Hour portal).
- USCIS: I-9 Q&A (Mar 28, 2025) allowing electronic signatures if controls met.
- NIST SP 800-63-4 (Aug 2025): Digital Identity Guidelines.
- Text Control adoption snapshot (Apr 2025): hybrid vs. fully digital usage.
- Adobe legal explainer: ESIGN Act overview (2025).
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11 reference (e-records/e-signatures).
FAQ
Can we sign Form I-9 electronically?
Yes, you can if your solution meets 8 C.F.R. § 274a.2(e)–(i) standards and preserves content, sequence, and auditability. USCIS explicitly explains how employers can implement electronic I-9 with electronic signatures.
What identity strength should we require for HR signatures?
Use risk-based steps: lower-risk policy acknowledgments may use email link + SMS; wage/tax/benefits may warrant stronger authenticators aligned with NIST SP 800-63-4.
How do e-signatures support DOL recordkeeping?
They centralize accurate timestamps, signer identity, and document versions, making it easier to meet FLSA recordkeeping and audit needs.
What’s the #1 pitfall of eSignature workflows for HR?
Hybrid workflows without audit trails. Standardize templates, set signer authentication by risk, and ensure exportable audit files.
- Current state & trends in HR e-signatures
- Statistics & dynamics HR leaders should know
- What to evaluate in an HR e-signature platform)
- Impact on stakeholders
- Expert forecasts (6–24 months, USA)
- Use cases
- Practical how-to: stand up HR e-signatures in 30 days
- How SignNow fits real HR workflows: practical patterns
- Conclusion
- FAQ