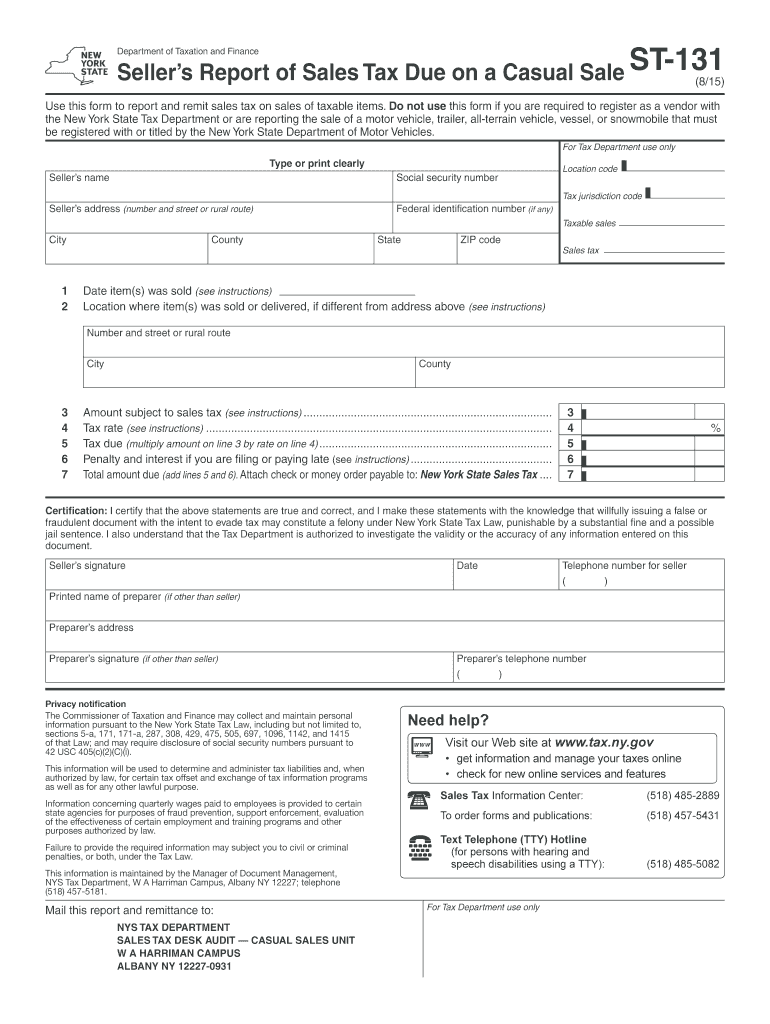
Form ST 131815 Sellers Report of Sales Tax Due on a Casual 2015


What is the Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual
The Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual is a tax document used in the United States for reporting sales tax obligations related to casual sales. Casual sales typically refer to transactions that are not part of a regular business operation, such as occasional sales by individuals or small entities. This form helps ensure compliance with state sales tax regulations by providing a structured way for sellers to report and remit the appropriate sales tax collected from buyers.
How to use the Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual
Using the Form ST 131815 involves several straightforward steps. First, gather all necessary information about the sales made, including the total sales amount and the sales tax collected. Next, accurately fill out the form, ensuring that all required fields are completed. After completing the form, it can be submitted either electronically or via traditional mail, depending on state-specific guidelines. It is essential to retain a copy of the submitted form for your records.
Steps to complete the Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual
Completing the Form ST 131815 requires careful attention to detail. Follow these steps for accurate submission:
- Collect all relevant sales data, including dates, amounts, and tax rates.
- Access the form online or obtain a physical copy from your local tax authority.
- Fill in your personal information, including name and address.
- Report the total sales amount and the corresponding sales tax collected.
- Review the form for accuracy before submission.
- Submit the completed form according to your state’s guidelines, either online or by mail.
Legal use of the Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual
The legal use of the Form ST 131815 is crucial for compliance with state tax laws. This form serves as an official record of sales tax collected on casual sales, which is necessary for accurate reporting and remittance to tax authorities. Failure to file this form correctly may result in penalties or legal repercussions. Therefore, it is important to understand the specific legal requirements related to casual sales in your state and ensure that the form is completed in accordance with those regulations.
Filing Deadlines / Important Dates
Filing deadlines for the Form ST 131815 can vary by state, but it is generally required to be submitted on a regular schedule, such as monthly or quarterly. It is essential to be aware of these deadlines to avoid late fees or penalties. Taxpayers should check with their state tax authority for specific due dates and any applicable grace periods for filing the form.
Form Submission Methods (Online / Mail / In-Person)
The Form ST 131815 can typically be submitted through various methods, including online submission, mailing a physical copy, or in-person delivery to the appropriate tax office. Online submission is often the fastest and most efficient method, allowing for immediate processing. When mailing the form, ensure it is sent to the correct address and consider using a trackable mailing service for confirmation of delivery. In-person submissions may be available at local tax offices during business hours.
Quick guide on how to complete form st 131815 sellers report of sales tax due on a casual
Your assistance manual on how to prepare your Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual
If you’re curious about how to finish and submit your Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual, here are some quick tips to simplify the tax declaration process.
Firstly, you just need to set up your airSlate SignNow account to transform the way you manage documents online. airSlate SignNow is a highly user-friendly and efficient document platform that allows you to modify, create, and finalize your tax documents without difficulty. With its editor, you can easily toggle between text, checkboxes, and eSignatures and return to adjust information as necessary. Streamline your tax management with sophisticated PDF editing, eSigning, and easy sharing options.
Follow these instructions to complete your Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual in just a few minutes:
- Establish your account and begin working on PDFs right away.
- Utilize our library to locate any IRS tax form; review various versions and schedules.
- Click Get form to launch your Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual in our editor.
- Complete the necessary fillable fields with your details (text, numbers, checkmarks).
- Employ the Sign Tool to include your legally-recognized eSignature (if necessary).
- Review your document and correct any errors.
- Save modifications, print your copy, send it to your recipient, and download it to your device.
Utilize this manual to electronically file your taxes with airSlate SignNow. Keep in mind that submitting in writing can lead to more mistakes on returns and postpone reimbursements. Certainly, before electronically filing your taxes, consult the IRS website for declaration guidelines in your state.
Create this form in 5 minutes or less
Find and fill out the correct form st 131815 sellers report of sales tax due on a casual
FAQs
-
How does the IRS validate the amount of sales a vendor made at the Farmer's Market in California on any given day and how do sellers report tax?
The IRS doesn't validate it. Selling at the farmer's market is a good way to earn cash that nobody knows about.They don't waster resources going after farmer's market sellers. The amounts are so small that they probably wold not be taxed.You self report. I'd do it on Form 1040, Sched. C. If it's a small amount, as misc income.
-
If a foreign citizen lives in the US on a working visa for more than a year, then what is his status? What tax form will such a person fill out when filing for taxes at the end of the tax year? Is the 1040NR the form to fill out?
In most situations, a person who is physically present in the United States for at least 183 days out of any calendar year is a US resident for tax purposes and must file Form 1040 as a tax resident. There are exceptions to this general rule, but none of them apply to people who are present in the United States in H-1B (guest worker) status. Furthermore, H-1B workers are categorically resident aliens for tax purposes and must pay taxes on the income they earn while in H-1B status as a resident alien in every year in which they earn more than the personal exemption limit. This includes both the first year and last year, even if the first or last year contains less than 183 days of residence in the United States. The short years may result in a filing as a “dual-status” alien.An H-1B worker will therefore only file Form 1040NR as his or her primary tax return in the tax year in which he or she leaves the United States permanently, and all US-connected income during that year will be taxed as if the taxpayer was a US resident, under the dual-status rules. All other tax returns during that person’s residence in the United States will be on Form 1040. The first year’s return may be under dual-status rules, with a Form 1040NR attached as a “dual status statement” as per the procedure in Chapter 6 of Publication 519 (2016), U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens. A person who resides the entire year in the United States in H-1B status may not use Form 1040NR, and is required to pay US income tax on his or her worldwide income, excepting only that income which is subject to protection under a tax treaty.See Publication 519 (2016), U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens for more information. The use of a tax professional, especially in the first and last year of H-1B status, is highly recommended as completing a dual-status return correctly is exceedingly challenging.
-
Why should it be so complicated just figuring out how much tax to pay? (record keeping, software, filling out forms . . . many times cost much more than the amount of taxes due) The cost of compliance makes the U.S. uncompetitive and costs jobs and lowers our standard of living.
Taxes can be viewed as having 4 uses (or purposes) in our (and most) governments:Revenue generation (to pay for public services).Fiscal policy control (e.g., If the government wishes to reduce the money supply in order to reduce the risk of inflation, they can raise interest rates, sell fewer bonds, burn money, or raise taxes. In the last case, this represents excess tax revenue over the actual spending needs of the government).Wealth re-distribution. One argument for this is that the earnings of a country can be perceived as belonging to all of its citizens since the we all have a stake in the resources of the country (natural resources, and intangibles such as culture, good citizenship, civic duties). Without some tax policy complexity, the free market alone does not re-distribute wealth according to this "shared" resources concept. However, this steps into the boundary of Purpose # 4...A way to implement Social Policy (and similar government mandated policies, such as environmental policy, health policy, savings and debt policy, etc.). As Government spending can be use to implement policies (e.g., spending money on public health care, environmental cleanup, education, etc.), it is equivalent to provide tax breaks (income deductions or tax credits) for the private sector to act in certain ways -- e.g., spend money on R&D, pay for their own education or health care, avoid spending money on polluting cars by having a higher sales tax on these cars or offering a credit for trade-ins [ref: Cash for Clunkers]).Uses # 1 & 2 are rather straight-forward, and do not require a complex tax code to implement. Flat income and/or consumption (sales) taxes can easily be manipulated up or down overall for these top 2 uses. Furthermore, there is clarity when these uses are invoked. For spending, we publish a budget. For fiscal policy manipulation, the official economic agency (The Fed) publishes their outlook and agenda.Use # 3 is controversial because there is no Constitutional definition for the appropriate level of wealth re-distribution, and the very concept of wealth re-distribution is considered by some to be inappropriate and unconstitutional. Thus, the goal of wealth re-distribution is pretty much hidden in with the actions and policies of Use #4 (social policy manipulation).Use # 4, however, is where the complexity enters the Taxation system. Policy implementation through taxation (or through spending) occurs via legislation. Legislation (law making) is inherently complex and subject to gross manipulation by special interests during formation and amendments. Legislation is subject to interpretation, is prone to errors (leading to loopholes) and both unintentional or intentional (criminal / fraudulent) avoidance.The record keeping and forms referred to in the question are partially due to the basic formula for calculating taxes (i.e., percentage of income, cost of property, amount of purchase for a sales tax, ...). However, it is the complexity (and associated opportunities for exploitation) of taxation legislation for Use # 4 (Social Policy implementation) that naturally leads to complexity in the reporting requirements for the tax system.
-
As one of the cofounders of a multi-member LLC taxed as a partnership, how do I pay myself for work I am doing as a contractor for the company? What forms do I need to fill out?
First, the LLC operates as tax partnership (“TP”) as the default tax status if no election has been made as noted in Treasury Regulation Section 301.7701-3(b)(i). For legal purposes, we have a LLC. For tax purposes we have a tax partnership. Since we are discussing a tax issue here, we will discuss the issue from the perspective of a TP.A partner cannot under any circumstances be an employee of the TP as Revenue Ruling 69-184 dictated such. And, the 2016 preamble to Temporary Treasury Regulation Section 301.7701-2T notes the Treasury still supports this revenue ruling.Though a partner can engage in a transaction with the TP in a non partner capacity (Section 707a(a)).A partner receiving a 707(a) payment from the partnership receives the payment as any stranger receives a payment from the TP for services rendered. This partner gets treated for this transaction as if he/she were not a member of the TP (Treasury Regulation Section 1.707-1(a).As an example, a partner owns and operates a law firm specializing in contract law. The TP requires advice on terms and creation for new contracts the TP uses in its business with clients. This partner provides a bid for this unique job and the TP accepts it. Here, the partner bills the TP as it would any other client, and the partner reports the income from the TP client job as he/she would for any other client. The TP records the job as an expense and pays the partner as it would any other vendor. Here, I am assuming the law contract job represents an expense versus a capital item. Of course, the partner may have a law corporation though the same principle applies.Further, a TP can make fixed payments to a partner for services or capital — called guaranteed payments as noted in subsection (c).A 707(c) guaranteed payment shows up in the membership agreement drawn up by the business attorney. This payment provides a service partner with a guaranteed payment regardless of the TP’s income for the year as noted in Treasury Regulation Section 1.707-1(c).As an example, the TP operates an exclusive restaurant. Several partners contribute capital for the venture. The TP’s key service partner is the chef for the restaurant. And, the whole restaurant concept centers on this chef’s experience and creativity. The TP’s operating agreement provides the chef receives a certain % profit interest but as a minimum receives yearly a fixed $X guaranteed payment regardless of TP’s income level. In the first year of operations the TP has low profits as expected. The chef receives the guaranteed $X payment as provided in the membership agreement.The TP allocates the guaranteed payment to the capital interest partners on their TP k-1s as business expense. And, the TP includes the full $X guaranteed payment as income on the chef’s K-1. Here, the membership agreement demonstrates the chef only shares in profits not losses. So, the TP only allocates the guaranteed expense to those partners responsible for making up losses (the capital partners) as noted in Treasury Regulation Section 707-1(c) Example 3. The chef gets no allocation for the guaranteed expense as he/she does not participate in losses.If we change the situation slightly, we may change the tax results. If the membership agreement says the chef shares in losses, we then allocate a portion of the guaranteed expense back to the chef following the above treasury regulation.As a final note, a TP return requires knowledge of primary tax law if the TP desires filing a completed an accurate partnership tax return.I have completed the above tax analysis based on primary partnership tax law. If the situation changes in any manner, the tax outcome may change considerably. www.rst.tax
-
Assuming I collect sales tax from residents of all 50 states as an online seller, & send a check to each state annually, how do I avoid fines/penalties for technical bsignNowes (didn’t make estimated payments, use correct form, file quarterly etc.)?
Great question!To begin, you will only want to register for a sales tax permit in states where you have nexus. For states in which you have nexus, the best way to avoid fines/penalties due to technical bsignNowes is to either 1) pay early or 2) use a third party tool to automate your sales tax filings.That’s where a company like TaxJar comes in. TaxJar can automate your sales tax filings in every state so you never need to worry about deadlines, payments, fines, or forms again. TaxJar is able to do this by connecting with the places you sell via one-click integrations. Whether it’s a marketplace like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy or an eCommerce platform like Shopify, Magento, and Squarespace, TaxJar can get you set up in minutes.If you’re new to sales tax, I recommend reading TaxJar’s free guide to getting sales tax compliant in 2018. Whether you choose to use a third party tool or do it yourself, TaxJar’s free guide will get you moving in the right direction.
-
The Supreme Court has changed the sales tax landscape with the overturning of the physical presence rulings? How is a small on-line retailer to collect and report sales taxes for more than fifty jurisdictions? Is it time for a national sales tax?
I wrote this as a response to an article, but here it might be better.I see this decision as creating a bunch of problems.There are over 10,000 sales tax jurisdictions in the United States. Most of the states (~45) have a sales tax. In many states, cities and counties can add their own sales tax.First problem: city boundaries are not necessarily the same as mailing addresses. You can have a mailing address of a city, but not actually live in that city (meaning you can’t vote in the city’s elections, etc).Second problem: there are exempt goods. Food is often exempt from sales taxes, but sometimes snack food is taxed. In Connecticut, for instance, groceries are not taxed. If I buy a bag of chips at the deli, it’s taxed. If I buy 10 bags of the same chips at the grocery store, it’s not taxed. So for each geographical area, you’ll need to determine if that particular good is exempt from taxation.Third problem: changing rates. Tax rates change all the time. Many states have a tax free week (often in August, near back to school times), so you need to know that.Now, for the above, a brick and mortar store would know what municipality it was in, so it would need to deal with only one schedule, not 10,000+. They know when the tax holiday is, and what’s taxed and not taxed.But there’s a fundamental unfairness that the new tax has introduced. If I go to a store in New Hampshire and buy a refrigerator, and have it delivered to my house, there’s no sales tax. However, if I go online to the store’s site and order the same thing, that’s now taxed. When I go to a brick-and-mortar merchant, they only charge where they are, not where I live. But an online merchant needs to be aware of all these things.There are going to be probably two to four software producers for online merchants to process sales tax, and my bet is that they’ll charge more than the tax collected, at least for small to mid size businesses. Any business online that sells stuff is going to need to subscribe to a service to keep all these tax rates and how to calculate and where to send. It’s going to signNowly curtail online commerce among smaller merchants, forcing them to go through someplace like Amazon or through a sales tax calculation service, which will probably charge several dollars or percentage points per transaction. We have a super complicated sales tax structure in the United States, and now every online merchant has to conform with 10,000 constantly changing laws and rates.
-
How do I declare a short term capital gain tax in the ITR in India? I want to know about the ITR form number and where and what to fill in the details. This is my first time to pay a short term capital gain tax on an equity sale.
The selection of ITR form will depend upon the type of one's income.For Income from salary, house property, capital gains for ITR2 is suggestedHowever for income from above heads and business/profession ITR4 is suggestedIn both the forms under head CG, revenue from sale of equity shares are required to be mentioned along with purchase amount and expenses incurred on sale are also required to be mentioned.For short term and long term separate rows are there.Just fill up and it will take the net capital gain to respective cell in computation if income.
Create this form in 5 minutes!
How to create an eSignature for the form st 131815 sellers report of sales tax due on a casual
How to generate an eSignature for the Form St 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual in the online mode
How to generate an electronic signature for the Form St 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual in Google Chrome
How to generate an eSignature for putting it on the Form St 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual in Gmail
How to make an electronic signature for the Form St 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual from your smart phone
How to make an electronic signature for the Form St 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual on iOS
How to create an electronic signature for the Form St 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual on Android
People also ask
-
What is Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual?
Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual is a document used by sellers to report any sales tax due on casual sales. It simplifies the tax reporting process and ensures compliance with state regulations. Understanding this form is essential for businesses that engage in informal or infrequent sales.
-
How can airSlate SignNow help with Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual?
airSlate SignNow allows businesses to easily create, send, and eSign Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual. With user-friendly features, it streamlines document management and ensures timely submission. This leads to improved compliance and reduced administrative overhead.
-
Is there a cost associated with using airSlate SignNow for Form ST 131815?
Yes, airSlate SignNow offers various subscription plans tailored to fit different business needs, including pricing options that work well for those frequently dealing with Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual. The robust features provided make it a cost-effective choice for managing essential documents.
-
What features does airSlate SignNow provide for handling Form ST 131815?
airSlate SignNow includes features such as template creation, automated reminders, and secure eSignature capabilities for Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual. These functionalities enhance efficiency and ensure that all necessary steps are completed accurately and on time.
-
Can I integrate airSlate SignNow with other software for Form ST 131815 processing?
Absolutely! airSlate SignNow supports integration with various software applications, optimizing your workflow for handling Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual. This allows for seamless data transfer and enhanced collaborative efforts across different platforms.
-
How does using airSlate SignNow benefit my business with Form ST 131815?
Using airSlate SignNow to manage Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual provides signNow benefits such as improved efficiency, reduced paper usage, and enhanced compliance. Your team can focus on core tasks rather than administrative hurdles, knowing that tax reporting is handled professionally.
-
Is it easy to learn how to use airSlate SignNow for Form ST 131815?
Yes, airSlate SignNow is designed with user-friendliness in mind. Both newcomers and experienced users find it easy to navigate and utilize its features for Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual, ensuring a smooth transition into digital document management.
Get more for Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual
- Bridgeport ct personal property declaration form
- Belle river high volunteer hours form
- Va form 3036
- Kapsabet girls sc ke student login form
- Francis lewis email form
- National grid non residential application form
- Www pdffiller com525151225 tlingit and haidatlingit and haida cares act fill online printable form
- Rsw exemption form bristol bay borough
Find out other Form ST 131815 Sellers Report Of Sales Tax Due On A Casual
- How Can I eSign Wyoming Real Estate Form
- How Can I eSign Hawaii Police PDF
- Can I eSign Hawaii Police Form
- How To eSign Hawaii Police PPT
- Can I eSign Hawaii Police PPT
- How To eSign Delaware Courts Form
- Can I eSign Hawaii Courts Document
- Can I eSign Nebraska Police Form
- Can I eSign Nebraska Courts PDF
- How Can I eSign North Carolina Courts Presentation
- How Can I eSign Washington Police Form
- Help Me With eSignature Tennessee Banking PDF
- How Can I eSignature Virginia Banking PPT
- How Can I eSignature Virginia Banking PPT
- Can I eSignature Washington Banking Word
- Can I eSignature Mississippi Business Operations Document
- How To eSignature Missouri Car Dealer Document
- How Can I eSignature Missouri Business Operations PPT
- How Can I eSignature Montana Car Dealer Document
- Help Me With eSignature Kentucky Charity Form