How Can I Sign Massachusetts Banking Form
Contact Sales
Make the most out of your eSignature workflows with airSlate SignNow
Extensive suite of eSignature tools
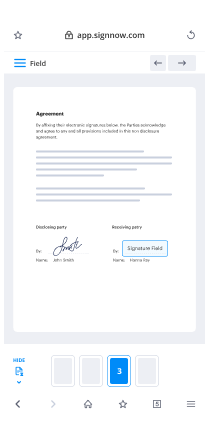
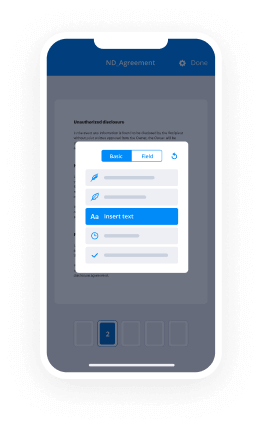
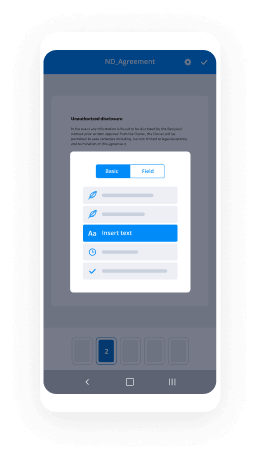
Discover the easiest way to Sign Massachusetts Banking Form with our powerful tools that go beyond eSignature. Sign documents and collect data, signatures, and payments from other parties from a single solution.
Robust integration and API capabilities
Enable the airSlate SignNow API and supercharge your workspace systems with eSignature tools. Streamline data routing and record updates with out-of-the-box integrations.
Advanced security and compliance
Set up your eSignature workflows while staying compliant with major eSignature, data protection, and eCommerce laws. Use airSlate SignNow to make every interaction with a document secure and compliant.
Various collaboration tools
Make communication and interaction within your team more transparent and effective. Accomplish more with minimal efforts on your side and add value to the business.
Enjoyable and stress-free signing experience
Delight your partners and employees with a straightforward way of signing documents. Make document approval flexible and precise.
Extensive support
Explore a range of video tutorials and guides on how to Sign Massachusetts Banking Form. Get all the help you need from our dedicated support team.
How can i industry sign banking massachusetts form online
Keep your eSignature workflows on track
Make the signing process more streamlined and uniform
Take control of every aspect of the document execution process. eSign, send out for signature, manage, route, and save your documents in a single secure solution.
Add and collect signatures from anywhere
Let your customers and your team stay connected even when offline. Access airSlate SignNow to Sign Massachusetts Banking Form from any platform or device: your laptop, mobile phone, or tablet.
Ensure error-free results with reusable templates
Templatize frequently used documents to save time and reduce the risk of common errors when sending out copies for signing.
Stay compliant and secure when eSigning
Use airSlate SignNow to Sign Massachusetts Banking Form and ensure the integrity and security of your data at every step of the document execution cycle.
Enjoy the ease of setup and onboarding process
Have your eSignature workflow up and running in minutes. Take advantage of numerous detailed guides and tutorials, or contact our dedicated support team to make the most out of the airSlate SignNow functionality.
Benefit from integrations and API for maximum efficiency
Integrate with a rich selection of productivity and data storage tools. Create a more encrypted and seamless signing experience with the airSlate SignNow API.
Collect signatures
24x
faster
Reduce costs by
$30
per document
Save up to
40h
per employee / month
Our user reviews speak for themselves






-
Best ROI. Our customers achieve an average 7x ROI within the first six months.
-
Scales with your use cases. From SMBs to mid-market, airSlate SignNow delivers results for businesses of all sizes.
-
Intuitive UI and API. Sign and send documents from your apps in minutes.
A smarter way to work: —how to industry sign banking integrate
Trusted esignature solution— what our customers are saying
be ready to get more
Get legally-binding signatures now!
Related searches to How Can I Sign Massachusetts Banking Form
Frequently asked questions
How do i add an electronic signature to a word document?
When a client enters information (such as a password) into the online form on , the information is encrypted so the client cannot see it. An authorized representative for the client, called a "Doe Representative," must enter the information into the "Signature" field to complete the signature.
How to sign a document through a pdf?
How to sign through the Internet? What is a pdf document? How to send and receive a pdf document? How to create a pdf document? How to sign a pdf document using the Internet? If the PDF document is not saved in the folder, how to save the file in another folder?
How to create a PDF for the website? To sign a PDF in a computer, how to sign the pdf document through computer? Which programs will I need to use to create a PDF?
How to create a PDF in an electronic book?
How to create a pdf in Windows PowerPoint?
For more than the above information, do not forget to check our PDF tutorial to become an expert in the subject.
?
Get more for How Can I Sign Massachusetts Banking Form
- Sign Vermont Car Dealer Limited Power Of Attorney Mobile
- Sign Vermont Car Dealer Limited Power Of Attorney Now
- Sign Vermont Car Dealer Limited Power Of Attorney Later
- Help Me With Sign Vermont Car Dealer Forbearance Agreement
- Sign Texas Car Dealer Medical History Online
- Sign Vermont Car Dealer Limited Power Of Attorney Myself
- Sign Vermont Car Dealer Limited Power Of Attorney Free
- Sign Texas Car Dealer Medical History Computer
Find out other How Can I Sign Massachusetts Banking Form
- Hipaa form pdf
- Manulife gl3585e fillable form
- Commercial travelers mutual insurance company form
- Medical hampampp preop form
- Sentry 401k form
- Mwhc form
- Manulife claim form 461773742
- Umc health system patient label here adult discharge plan form
- Earlylearningwa form
- Johns creek psychology confidential patient questionnaire form
- Youth sports physical form
- Skin type worksheet skin renew clinic form
- Cenikor forms
- Tb documentation form
- Renewal by synergy cerps log american association of critical bb aacn form
- Letter of support for individuals with no income or no form
- Child care classroom refrigerator temperature log form
- Hg new wax intake form hey gorgeous waxing and skin studio
- Micropigmentation consent form
- Face to face physician encounter form