eSignature Lawfulness for Accounting and Tax in Australia
- Quick to start
- Easy-to-use
- 24/7 support
Simplified document journeys for small teams and individuals



We spread the word about digital transformation
Why choose airSlate SignNow
-
Free 7-day trial. Choose the plan you need and try it risk-free.
-
Honest pricing for full-featured plans. airSlate SignNow offers subscription plans with no overages or hidden fees at renewal.
-
Enterprise-grade security. airSlate SignNow helps you comply with global security standards.







Your complete how-to guide - e signature lawfulness for accounting and tax in australia
eSignature Lawfulness for Accounting and Tax in Australia
In today's digital age, it is crucial to understand the eSignature lawfulness for Accounting and Tax in Australia. By using airSlate SignNow, businesses can ensure compliance while streamlining their document signing processes.
Steps to utilize airSlate SignNow for eSignatures:
- Launch the airSlate SignNow web page in your browser.
- Sign up for a free trial or log in.
- Upload a document you want to sign or send for signing.
- Convert your document into a template for future use.
- Edit your file by adding fillable fields or necessary information.
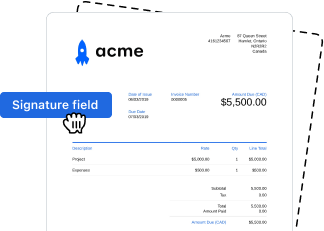
- Sign the document and add signature fields for recipients.
- Click Continue to set up and send an eSignature invite.
airSlate SignNow empowers businesses to streamline their document signing processes with an easy-to-use and cost-effective solution. It offers great ROI with a rich feature set, tailored for SMBs and Mid-Market. The platform also provides transparent pricing without hidden support fees and add-on costs, along with superior 24/7 support for all paid plans.
Experience the benefits of airSlate SignNow today and revolutionize how you handle eSignatures for your Accounting and Tax documents in Australia.
How it works
Rate your experience
What is the electronic signature for accountants
An electronic signature for accountants is a digital representation of a signature that allows accountants to sign documents electronically. This method streamlines the signing process, making it faster and more efficient than traditional paper-based signatures. With electronic signatures, accountants can sign tax documents, financial statements, and contracts securely and conveniently, reducing the need for physical paperwork.
How to use the electronic signature for accountants
Using an electronic signature for accountants involves a few straightforward steps. First, accountants can upload the document they need to sign onto the airSlate SignNow platform. Next, they can fill out any required fields directly within the document. Once the document is ready, accountants can click to sign electronically, either by drawing their signature, typing it, or using a pre-saved signature. After signing, the document can be sent to clients or colleagues for their signatures, creating a seamless workflow.
Legal use of the electronic signature for accountants
Electronic signatures are legally recognized in the United States under the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act and the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA). These laws ensure that electronic signatures hold the same legal weight as traditional signatures, provided that both parties consent to use electronic means for signing. Accountants can confidently use electronic signatures for various documents, including tax returns and contracts, knowing they comply with legal standards.
Steps to complete the electronic signature for accountants
Completing an electronic signature for accountants involves several key steps:
- Upload the document to the airSlate SignNow platform.
- Fill in any necessary information or fields within the document.
- Select the option to eSign and choose your preferred method of signing.
- Review the document to ensure all information is correct.
- Send the document for signature to clients or colleagues if needed.
- Save or download the signed document for your records.
Security & Compliance Guidelines
When using electronic signatures, security and compliance are paramount. airSlate SignNow employs advanced encryption methods to protect sensitive information during transmission and storage. Additionally, the platform complies with industry standards and legal regulations, ensuring that all electronic signatures are secure and verifiable. Accountants should ensure that they follow best practices, such as using strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication, to further enhance security.
Examples of using the electronic signature for accountants
Accountants can utilize electronic signatures in various scenarios, including:
- Signing tax returns and filings to expedite submission.
- Approving financial statements and reports for clients.
- Finalizing contracts and agreements with vendors or clients.
- Obtaining client approvals for accounting services or fees.
Documents You Can Sign
Accountants can sign a wide range of documents electronically, including:
- Tax returns and related forms.
- Financial statements and audit reports.
- Engagement letters and service agreements.
- Invoices and payment authorizations.
-
Best ROI. Our customers achieve an average 7x ROI within the first six months.
-
Scales with your use cases. From SMBs to mid-market, airSlate SignNow delivers results for businesses of all sizes.
-
Intuitive UI and API. Sign and send documents from your apps in minutes.
FAQs
-
What is an electronic signature for accountants?
An electronic signature for accountants is a digital representation of a signature that allows accountants to sign documents electronically. This method streamlines the signing process, making it faster and more efficient while ensuring compliance with legal standards.
-
How does airSlate SignNow enhance the electronic signature for accountants?
airSlate SignNow enhances the electronic signature for accountants by providing a user-friendly platform that simplifies document management. With features like templates, automated workflows, and secure storage, accountants can focus more on their work and less on paperwork.
-
What are the pricing options for airSlate SignNow's electronic signature for accountants?
airSlate SignNow offers flexible pricing plans tailored for accountants, ensuring cost-effectiveness. You can choose from monthly or annual subscriptions, with options that scale based on the number of users and features needed, making it accessible for firms of all sizes.
-
Is airSlate SignNow compliant with legal standards for electronic signatures?
Yes, airSlate SignNow's electronic signature for accountants complies with major legal standards, including the ESIGN Act and UETA. This compliance ensures that your electronically signed documents are legally binding and recognized in court.
-
What features does airSlate SignNow offer for accountants?
airSlate SignNow offers a variety of features tailored for accountants, including customizable templates, bulk sending, and real-time tracking of document status. These features help streamline the signing process and improve overall efficiency in document management.
-
Can airSlate SignNow integrate with other accounting software?
Absolutely! airSlate SignNow's electronic signature for accountants can seamlessly integrate with popular accounting software like QuickBooks and Xero. This integration allows for a smoother workflow, enabling accountants to manage documents directly within their preferred platforms.
-
What are the benefits of using electronic signatures for accountants?
Using electronic signatures for accountants offers numerous benefits, including reduced turnaround time for document signing, enhanced security, and improved client satisfaction. By adopting airSlate SignNow, accountants can streamline their processes and focus on delivering exceptional service.
Join over 28 million airSlate SignNow users
Get more for e signature lawfulness for accounting and tax in australia
- Edit PDFs and Sign Online with airSlate SignNow
- Unlock the Secret to Adding Signatures to PDFs Easily
- Discover How to Add Signature in Editable PDF Easily ...
- Streamline Your Workflow with the Best Email Signature ...
- How to Modify a Signed PDF Easily with airSlate SignNow
- How to Edit Signature on PDF with airSlate SignNow
- Unlock Business Efficiency with our Signature Drawer ...
- Get Your PDFs Digitally Signed by Experts in Minutes