Signed Indemnity Agreement Made Easy
Do more online with a globally-trusted eSignature platform
Outstanding signing experience
Reliable reporting and analytics
Mobile eSigning in person and remotely
Industry regulations and compliance
Signed indemnity agreement, quicker than ever before
Helpful eSignature extensions
See airSlate SignNow eSignatures in action
airSlate SignNow solutions for better efficiency
Our user reviews speak for themselves






Why choose airSlate SignNow
-
Free 7-day trial. Choose the plan you need and try it risk-free.
-
Honest pricing for full-featured plans. airSlate SignNow offers subscription plans with no overages or hidden fees at renewal.
-
Enterprise-grade security. airSlate SignNow helps you comply with global security standards.

Your step-by-step guide — signed indemnity agreement
Adopting airSlate SignNow’s electronic signature any company can enhance signature workflows and sign online in real-time, giving a better experience to customers and staff members. Use signed Indemnity Agreement in a few simple actions. Our mobile-first apps make operating on the run possible, even while off-line! eSign contracts from anywhere in the world and close trades in less time.
Take a stepwise guideline for using signed Indemnity Agreement:
- Log on to your airSlate SignNow profile.
- Locate your record within your folders or import a new one.
- Open the document and make edits using the Tools list.
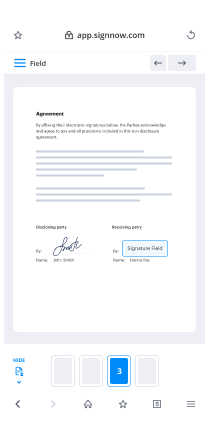
- Drag & drop fillable boxes, add text and sign it.
- Include several signees using their emails and set the signing sequence.
- Choose which users will receive an executed version.
- Use Advanced Options to restrict access to the template add an expiration date.
- Click Save and Close when done.
Furthermore, there are more advanced features open for signed Indemnity Agreement. List users to your collaborative digital workplace, browse teams, and monitor cooperation. Millions of people across the US and Europe concur that a solution that brings people together in one cohesive workspace, is the thing that enterprises need to keep workflows performing efficiently. The airSlate SignNow REST API allows you to embed eSignatures into your app, website, CRM or cloud storage. Try out airSlate SignNow and get faster, smoother and overall more effective eSignature workflows!
How it works
airSlate SignNow features that users love
See exceptional results signed Indemnity Agreement made easy
Get legally-binding signatures now!
FAQs
-
What is the indemnity agreement?
Indemnity is considered to be a contractual agreement between two parties whereby one party agrees to pay for potential losses or damages caused by another party. ... With indemnity, the insurer indemnifies the policyholder\u2014that is, promises to make whole the individual or business for any covered loss. -
How does an indemnity work?
Indemnity refers in some contexts as compensation for loss or damage from the actions of another party. Indemnity can also refer to a legal exemption from loss or damages, as in the case of an indemnity clause in a contract, in which one party agrees to take the liability for loss or damage from another party. -
Should you sign a hold harmless agreement?
By signing a broad form hold harmless agreement you are possibly exposing your company to uninsurable risk. Contractual Liability Coverage for sole or gross negligent acts of your client is excluded is y most liability policies. ... As with all contracts, it is best to have legal counsel review prior to signing. -
What happens when you indemnify someone?
To indemnify someone is to absolve that person from responsibility for damage or loss arising from a transaction. Indemnification is the act of not being held liable for or being protected from harm, loss, or damages, by shifting the liability to another party. -
What is the purpose of an indemnification agreement?
An indemnity agreement is a contract that 'holds a business or company harmless' for any burden, loss, or damage. An indemnity agreement also ensures proper compensation is available for such loss or damage. -
What does the legal term indemnify mean?
Indemnify Law and Legal Definition. To indemnify means to reimburse another for a loss suffered because of a third party's or one's own act or default. ... The right to indemnity and the duty to indemnify commonly comes from a contractual agreement, which generally protects against liability, loss, or damage. -
How do you get an indemnity bond?
To execute or redeem an indemnity bond, the claimant or principal must comply with the terms of the indemnity bond. In most cases, the claimant must provide written notice that the obligor has failed to perform under the contract, and the claimant is looking to the guarantor or issuer of the indemnity bond for payment.