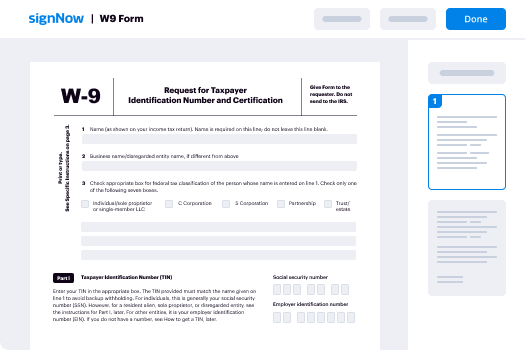
Electronic signature Word for Administrative Mobile
Make the most out of your eSignature workflows with airSlate SignNow
Extensive suite of eSignature tools
Discover the easiest way to Electronic signature Word for Administrative Mobile with our powerful tools that go beyond eSignature. Sign documents and collect data, signatures, and payments from other parties from a single solution.
Robust integration and API capabilities
Enable the airSlate SignNow API and supercharge your workspace systems with eSignature tools. Streamline data routing and record updates with out-of-the-box integrations.
Advanced security and compliance
Set up your eSignature workflows while staying compliant with major eSignature, data protection, and eCommerce laws. Use airSlate SignNow to make every interaction with a document secure and compliant.
Various collaboration tools
Make communication and interaction within your team more transparent and effective. Accomplish more with minimal efforts on your side and add value to the business.
Enjoyable and stress-free signing experience
Delight your partners and employees with a straightforward way of signing documents. Make document approval flexible and precise.
Extensive support
Explore a range of video tutorials and guides on how to Electronic signature Word for Administrative Mobile. Get all the help you need from our dedicated support team.
Keep your eSignature workflows on track
Make the signing process more streamlined and uniform
Take control of every aspect of the document execution process. eSign, send out for signature, manage, route, and save your documents in a single secure solution.
Add and collect signatures from anywhere
Let your customers and your team stay connected even when offline. Access airSlate SignNow to Electronic signature Word for Administrative Mobile from any platform or device: your laptop, mobile phone, or tablet.
Ensure error-free results with reusable templates
Templatize frequently used documents to save time and reduce the risk of common errors when sending out copies for signing.
Stay compliant and secure when eSigning
Use airSlate SignNow to Electronic signature Word for Administrative Mobile and ensure the integrity and security of your data at every step of the document execution cycle.
Enjoy the ease of setup and onboarding process
Have your eSignature workflow up and running in minutes. Take advantage of numerous detailed guides and tutorials, or contact our dedicated support team to make the most out of the airSlate SignNow functionality.
Benefit from integrations and API for maximum efficiency
Integrate with a rich selection of productivity and data storage tools. Create a more encrypted and seamless signing experience with the airSlate SignNow API.
Collect signatures
24x
faster
Reduce costs by
$30
per document
Save up to
40h
per employee / month
Our user reviews speak for themselves






How to utilize Word on mobile
If you’re aiming to improve your document signing process while on the move, discovering how to utilize Word on mobile can signNowly elevate your experience. With airSlate SignNow, you can effortlessly oversee electronic signatures and document workflows directly from your phone or tablet. This guide will guide you through the straightforward steps to get started.
Steps to utilize Word on mobile with airSlate SignNow
- Access the airSlate SignNow website in your mobile browser.
- Set up a free account or log into your current account.
- Upload the document you intend to sign or send for signatures.
- If you intend to reuse the document, save it as a template.
- Open the document and make required edits, such as including fillable fields.
- Affix your signature to the document and assign signature fields for your recipients.
- Click 'Continue' to prepare and dispatch an eSignature invitation.
Using airSlate SignNow offers businesses a strong solution for document management and electronic signing. Its intuitive interface and powerful features render it an excellent option for both small and medium-sized enterprises.
Prepared to simplify your document signing procedure? Begin your free trial with airSlate SignNow today and enjoy unmatched support and clear pricing!
How it works
Upload & open your document in the editor
Fill it out and eSign it in minutes
Save the signed document or share it with others
Rate your experience
-
Best ROI. Our customers achieve an average 7x ROI within the first six months.
-
Scales with your use cases. From SMBs to mid-market, airSlate SignNow delivers results for businesses of all sizes.
-
Intuitive UI and API. Sign and send documents from your apps in minutes.
A smarter way to work: —how to industry sign banking integrate
FAQs
-
How can I use Word on mobile with airSlate SignNow?
To effectively use Word on mobile with airSlate SignNow, simply download the airSlate SignNow app from your device's app store. Once installed, you can easily upload Word documents and send them for electronic signatures. This seamless integration allows you to work on your documents anytime and anywhere.
-
What features does airSlate SignNow offer for using Word on mobile?
When you use Word on mobile with airSlate SignNow, you gain access to features like document editing, eSignature capabilities, and real-time collaboration. These tools empower you to manage your documents efficiently while on the go, ensuring that you can complete important tasks without being tied to a desktop.
-
Is airSlate SignNow compatible with different mobile devices for using Word?
Yes, airSlate SignNow is highly compatible with various mobile devices, including iOS and Android smartphones and tablets. This compatibility makes it easy to use Word on mobile, allowing you to manage your documents and sign them from virtually any device.
-
What are the pricing options for using airSlate SignNow to work with Word on mobile?
airSlate SignNow offers flexible pricing plans suitable for individuals and businesses of all sizes. Whether you're looking for a basic plan or advanced features, you can choose the best option that fits your needs for using Word on mobile. Explore our pricing page to find the perfect plan for you.
-
Can I integrate airSlate SignNow with other apps while using Word on mobile?
Absolutely! airSlate SignNow allows you to integrate with various applications while using Word on mobile. This enables you to streamline your workflow, making it easier to manage and send documents for eSigning alongside your other favorite tools.
-
What are the benefits of using airSlate SignNow to eSign Word documents on mobile?
Using airSlate SignNow to eSign Word documents on mobile offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, mobility, and security. You can quickly sign documents without delays, ensuring that your business processes remain smooth and uninterrupted, even when you're away from your desk.
-
How secure is it to use Word on mobile with airSlate SignNow?
Security is a top priority for airSlate SignNow. When you use Word on mobile, all documents are protected with industry-standard encryption and secure access controls. This ensures that your sensitive information remains safe while you manage and sign documents from any location.
-
Who are the 2013 Top Writers on Quora?
I am, strangely enough. My output has waned over the last year as I've become busier. But I'm happy to take the fleece. In the meantime, enjoy some of my greatest hits of the past year, most of which are not that great: Biology * Shan Kothari's answer to Is it a good idea to interbreed the various endangered tiger subspecies like the Sumatran, Malayan, Indo-Chinese, South China, Bengal and Siberian tigers so that they have more genetic variation? [ https://www.quora.com/Is-it-a-good-idea-to-interbreed-the-various-endangered-tiger-subspecies-like-the-Sumatran-Malayan-Indo-Chinese-South-China-Bengal-and-Siberian-tigers-so-that-they-have-more-genetic-variation/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to Can giraffes swim? [ https://www.quora.com/Can-giraffes-swim/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to Ecology: What do ecologists think of Lotka-Volterra? [ https://www.quora.com/Ecology-What-do-ecologists-think-of-Lotka-Volterra/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to What is the future of big data in ecology? [ https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-future-of-big-data-in-ecology/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to What is hermatypic coral? [ https://www.quora.com/What-is-hermatypic-coral/answer/Shan-Kothari ] Philosophy * Shan Kothari's answer to Why did Blaise Pascal not immediately understand the "which god" problem with his wager? [ https://www.quora.com/Why-did-Blaise-Pascal-not-immediately-understand-the-which-god-problem-with-his-wager/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to Philosophy of Mind: What is functionalism? [ https://www.quora.com/Philosophy-of-Mind-What-is-functionalism/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to Do ethical philosophers tend to be more ethical? [ https://www.quora.com/Do-ethical-philosophers-tend-to-be-more-ethical/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to Can you be a philosopher and still believe in god? [ https://www.quora.com/Can-you-be-a-philosopher-and-still-believe-in-god/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to What are the main differences between epiphenomenalism and materialist reductionism? [ https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-main-differences-between-epiphenomenalism-and-materialist-reductionism/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to What has philosophy contributed to society in the past 50 years? [ https://www.quora.com/What-has-philosophy-contributed-to-society-in-the-past-50-years/answer/Shan-Kothari ] Other: * Shan Kothari's answer to What are some famous pictures that ruined people's lives? [ https://www.quora.com/What-are-some-famous-pictures-that-ruined-peoples-lives/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to Why is it common liberal policy to reject Social Darwinism despite wholeheartedly embracing evolution? Why this contradiction? [ https://www.quora.com/Why-is-it-common-liberal-policy-to-reject-Social-Darwinism-despite-wholeheartedly-embracing-evolution-Why-this-contradiction/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to Who are the best or most famous Christian poets? [ https://www.quora.com/Who-are-the-best-or-most-famous-Christian-poets/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to What are the most impressive intellectual achievements completed by persons under 20 years old in terms of the influence, magnitude, depth, scope, creativity, or difficulty of the achievement? [ https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-most-impressive-intellectual-achievements-completed-by-persons-under-20-years-old-in-terms-of-the-influence-magnitude-depth-scope-creativity-or-difficulty-of-the-achievement/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to What is it like to attend a REU? [ https://www.quora.com/What-is-it-like-to-attend-a-REU/answer/Shan-Kothari ] * Shan Kothari's answer to What directors chose the same people to work with time and time again, in any roles, and who are these people? [ https://www.quora.com/What-directors-chose-the-same-people-to-work-with-time-and-time-again-in-any-roles-and-who-are-these-people/answer/Shan-Kothari ]
-
Who are the Top Writers on Quora?
Balaji Viswanathan (பாலாஜி விஸ்வநாதன்)If ever you want to learn something new on daily basis.please switch on the notifications from Balaji Vishwanath sir.Awdhesh Singh (अवधेश सिंह)In case if you are wandering for the best views from an intellect,he is always on cards !Gopalkrishna VishwanathIf ever you wanted a simple answers with so much of life experience,don't forget to follow Gopalkrishna Vishwanath sir!Abhimanyu SoodIf you want to hear a story,please don't miss this guy.. he is my fav!User-9248814863030902883In case if you crave for travel experiences,this guy is fantastic ! Sinless bloke indeed.Sean KernanSarhad ChoudharyIn case if you are eager to know son and grandson of quora ..don't forget these wonderful guys !Vishak RamanIf you want to keep reading and getting lost.he is nice to read! Unique guy I must tell you !Dhawal BarotIf you seem very interested in shortest feel good stories,this guy tops the list!Loy MachedoWhenever you feel low,reading his answers can make you feel better!The list continues !And if ever you want to read some stupid answers follow this guy! Raghavendra MThanks for reading
-
How advanced is the Indian anti-missile system?
INDIAN AIR-DEFENSE SYSTEMSIndian forces have a wide array of Air Defense systems capable of providing cover to friendly airspace.The systems are operated by both the Indian Army and Indian Air Force.SYSTEMS IN USEAkash SAM: A Low-to-Medium level Medium Range Surface to Air Missile in service with both the Indian Army and Air Force. With maximum speed up to 2.5 Mach and altitude ranging from 0.5 to 18Km, it can successfully shoot down enemy drones, helicopters, fighters and even missiles. Guidance is through the ground-based 'Rajendra' radar which can track targets from 80km and engage from 60km. It is not vulnerable against Electronic Counter-Measures as the aircraft has to jam the high power 'Rajendra' radar to avoid getting git by Akash. It has clocked in high success rates in recent firing trials and would soon be inducted in more numbers.AKASH SAM during it's firing trials from ITRSA-6 or 2K12 'Kub': A Soviet-Era Low-to-Medium level SAM. This system has become nearly obsolete and would be soon phased out by Inducting more Akash systems. Capable of hitting targets up to 24km and effective altitude of 14km. the system can only guide one of two missiles at a time to a target whereas the Akash is capable of multiple missile guidance at the same time.SA-6 SAMSA-3 or S-125 'Pechora': Another piece of Soviet-era military tech which has become nearly obsolete in the current war scenario. The minimum range is 3.5 km, and the maximum is 35 km (with the Pechora 2A). The intercept altitudes are between 100 m and 18 km. It is in service with Indian Air force primarily for guarding Air bases until Akash systems are fully employed.SA-3 PechoraSA-5 or S-200: Is a Medium-to-High level very long range SAM employed to take out high flying bombers. It has a range from 150km to 300km and max speed of Mach 8. Guided mid-course by radio illumination and has a terminal radar homing phase. It has a very high single shot kill probability of 0.85 and is very effective against long-range bombers.S-200 SAMSA-8 'Gecko Mod-1' or 9K33 'OSA-AKM': Highly mobile, short range, low-level SAM of Soviet origin. The missile is mounted on an amphibious vehicle having its own radar and can act with or without the regimental surveillance radars. The range is about 15km and a maximum altitude of 12km.SA-8 Gecko during Republic Day paradeSA-13 'Gopher' or 9K35 'Strela 10M3': Highly mobile, low-level, short range SAM. The range of target destruction from 0.8km to 5km. Altitude ranging from 25m to 3500m.SA-13 GopherSA-19 'Grison' or 2K22 'Tunguska': The very famous 'Tunguska' is a mix of two different modes of air defense. It employs the 9M311 for engaging targets from 10km and the dual 2A38M cannons for engaging targets at close range (0.2 to 4km). The guns give out a combined rate of fire of about 4000-5000 rounds per minute. Indian Army has about 20-90 units in service.Indian Army TunguskaZSU-23-2 & ZSU-23-4 'Shilka': The former is a twin cannon Anti Air gun and the latter a Light armoured, Self-propelled, Anti-Aircraft gun. The number after 23 denotes the number of gun barrels. With 4x 3 mm 2A7 autocannons firing at 2000round per minute each, Shilka is used for low-level area defence. Effective against low flying drones and helicopters and is used to provide cover for infantry units. It is however ineffective as a modern short-range Air-Defense system but can be employed as a supporting system for infantry units.ZSU-23-4 ShilkaFIM-92 'Stinger': Is a Man-Portable Air-Defense System (MANPADS) SAM. Employs an Infrared seeker and can hit targets at 8km.US Military men firing the Stinger missile9K38 Igla: Russian equivalent to the American Stinger missiles. It too employs an Infrared seeker and can hit targets at 5.2km.Indian Army men with IglaBARAK-8: Is an advanced Indo-Israeli SAM capable of intercepting aircraft, helicopters, anti-ship missiles and cruise missiles. It was initially developed for use in Indian and Israeli ships against anti-ship missiles. It is one of the best Short-Medium range SAM systems in use now. There exists both naval and the land variant of these missiles. Operational range varies from 0.5km to 100km. An ER (Extended Range) variant is now developed and can hit targets up to 150km away. MRSAM version is under development and will provide a tiered airspace protection.Barak-8 and it's VLS cellSPYDER (Surface to Air PYthon and DERby): Is a low-level, quick-reaction surface-to-air missile system capable of engaging aircraft, helicopters, unmanned air vehicles, drones, and precision-guided munitions. It provides air defence for fixed assets and for point and area defence for mobile forces in combat areas. It employs the use of AAM (Air-to-Air Missiles) like Python and Derby to be fired from ground stations to provide air defence. SPYDER-MR engages targets at 35km and SPYDER-SR engages targets at 15km.Indian Air Force SPYDER SAMPrithvi Air Defense/Pradhyumna: Air-defense is not just to counter aircrafts but in this modern age of warfare, ballistic missiles pose a huge threat. It is a two stage missile with a maximum interception range of 80km. It is capable of attaining speeds over mach 5 and can successfully intercept ballistic missiles of 300-2000km range before it enters the atmosphere (Exospheric Interception).Indian BMD missile components and the mock target.Advanced Air Defense: Is an Endospheric anti-ballistic missile system capable of interception of targets at an altitude of 30km and can attain speeds over Mach 4.5. The PAD(Prithvi Air Defense) and AAD form the two tiers of India's Ballistic Missile Defense system. The development is underway and India has already entered the elite club of nations capable of intercepting Ballistic missiles after multiple success.The Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme is an initiative to develop and deploy a multi-layered ballistic missile defence system to protect from ballistic missile attacks.Launching of Advanced Air Defence (AAD) missilePrithvi Air Defence (PAD) / Pradyumna Ballistic Missile InterceptorThe Prithvi Air Defence (PAD) is an anti-ballistic missile developed to intercept incoming ballistic missiles outside the atmosphere (exo-atmospheric). Based on the Prithvi missile, PAD is a two-stage missile with a maximum interception altitude of 80 km (50 mi). The first stage is a Solid fuelled motor while the second stage is Liquid fuelled.It has manoeuvre thrusters which can generate a lateral acceleration of more than 5 gs at 50 km (31 mi) altitude. Guidance is provided by an intertial navigation system with mid-course updates from LRTR and active radar homing in the terminal phase.PAD has capability to engage the 300 to 2,000 km (190 to 1,240 mi) class of ballistic missiles at a speed of Mach 5.PAD is fast enough to hit medium-range ballistic missiles, but would struggles against intermediate-range ballistic missile types.LRTR is the target acquisition and fire control radar for the PAD missile. It is an active phased array radar having capability to track 200 targets at a range of 600 km (370 mi).The PAD missile has also been called Pradyumna.Advanced Air Defence (AAD)/Ashwin Ballistic Missile InterceptorAdvanced Air Defence (AAD) is an anti-ballistic missile designed to intercept incoming ballistic missiles in the endo-atmosphere at an altitude of 30 km (19 mi). AAD is a single-stage, solid-fuelled missile. Guidance is similar to that of PAD: it has an inertial navigation system, midcourse updates from ground-based radar and active radar homing in the terminal phase. It is 7.5 m (25 ft) tall, weighs around 1.2 t (1.2 long tons; 1.3 short tons) and a diameter of less than 0.5 m (1 ft 8 in).Swordfish RADARSwordfish is the target acquisition and fire control radar for the BMD system. The LRTR currently has a range of 600 km (370 mi) to 800 km (500 mi) and can spot objects as small as a cricket ball. The DRDO plans to upgrade the capacity of Swordfish to 1,500 km by 2011.Prithvi Defence Vehicle (PDV)In 2009, reports emerged of a new exo-atmospheric interceptor missile named the Prithvi Defence Vehicle (PDV) interceptor missile. The DRDO is developing a new Prithvi interceptor missile codenamed PDV. It will be a two-stage missile and both the stages will be powered by solid propellants. It will have an innovative system for controlling the vehicle at an altitude of more than 150 km The PDV is intended to replace the existing PAD in the PAD/AAD combination. It will have an IIR seeker for its kill vehicle as well. The PDV will replace the PAD with a far more capable missile and will complete the Phase 1 of the BMD system, allowing it to be operational by 2013. Whereupon Phase 2 development will take over for protection against missiles of the 5,000 km (3,100 mi)range class.The first test flight of the missile was expected in 2010.The PDV is designed to take out the target missile at altitudes above 150 km (93 mi).Akash (missile)Akash (Sanskrit: Ākāśa "Sky") is a medium-range mobile surface-to-air missile defense system developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and produced by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) for Missile Systems and Bharat Electronics(BEL) for other radars, control centers in India.The missile system can target aircraft up to 30 km away, at altitudes up to 18,000 m.It has the capability to "neutralise aerial targets like fighter jets, cruise missiles and air-to-surface missiles" as well as ballistic missiles.It is in operational service with the Indian Army and the Indian Air Force.An Akash battery comprises a single Rajendra 3D passive electronically scanned array radarand four launchers with three missiles each, all of which are interlinked. Each battery can track up to 64 targets and attack up to 12 of them. The missile has a 60 kg (130 lb) high-explosive, pre-fragmented warhead with a proximity fuse. The Akash system is fully mobile and capable of protecting a moving convoy of vehicles. The launch platform has been integrated with both wheeled and tracked vehicles. While the Akash system has primarily been designed as an air defence SAM, it also has been tested in a missile defense role. The system provides air defence missile coverage for an area of 2,000 km². The Indian military's combined orders of the Akash, including radar systems (WLR and Surveillance), have a total worth of ₹ 23,300 crore (US$4 billion).Akash SAM Missile at Defence ExpoAkash is a surface-to-air missile with an intercept range of 30 km.It has a launch weight of 720 kg, a diameter of 35 cm and a length of 5.78 metres. Akash flies at supersonic speed, signNowing around Mach 2.5. It can signNow an altitude of 18 km and can be fired from both tracked and wheeled platforms.An on-board guidance system coupled with an actuator system makes the missile maneuverable up to 15g loads and a tail chase capability for end game engagement. A digital proximity fuse is coupled with a 55 kg pre-fragmented warhead, while the safety arming and detonation mechanism enables a controlled detonation sequence. A self-destruct device is also integrated. It is propelled by an Integrated Ramjet Rocket Engine. The use of a ramjet propulsion system enables sustained speeds without deceleration throughout its flight.The Missile has command guidance in its entire flight.Barak 8Indian-Israeli surface-to-air missileBarak 8 (the Hebrew word for Lightning) also known as LR-SAM or as MR-SAMis an Indian-Israeli surface-to-air missile (SAM), designed to defend against any type of airborne threat including aircraft, helicopters, anti-ship missiles, and UAVs as well as ballistic missiles, cruise missiles and combat jets.Both maritime and land-based versions of the system exist.Barak 8 was jointly developed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), India's Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), Israel's Administration for the Development of Weapons and Technological Infrastructure, Elta Systems, Rafael and other companies. Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) produce the missiles.INS Kolkata firing a Barak 8 missileBarak 8 launcher moduleThe Barak 8 has a length of about 4.5 meters, a diameter of 0.225 meters at missile body, and 0.54 meters at the booster stage, a wingspan of 0.94 meters and weighs 275 kg including a 60 kg warhead which detonates at proximity. The missile has maximum speed of Mach 2 with a maximum operational range of 70 km,which was later increased to 100 km.Barak 8 features a dual pulse rocket motor as well as Thrust vector control,and possesses high degrees of maneuverability at target interception range. A second motor is fired during the terminal phase, at which stage the active radar seekeris activated to home in on to the enemy track. Barak 8 has been designed to counter a wide variety of air-borne threats, such as; anti-ship missiles, aircraft, UAVs drones and supersonic missilesWhen coupled with a modern air-defence system and multi-function surveillance track and guidance radars, (such as the EL/M-2248 MF-STAR AESA on board the Kolkata-class destroyers) Barak 8 enables the capability to simultaneously engage multiple targets during saturation attacks.Israel Aerospace Industries describe Barak 8 as "an advanced, long-range missile defense and air defense system" with its main features being:Long RangeTwo way data link (GPS S band)Active Radar Seeker Missile360 degree coverageVertical LaunchMultiple Simultaneous EngagementsPoint defence anti-ballistic missileMRSAMMRSAM is the land based configuration of the missile. It consists of a command and control system, tracking radar, missile and mobile launcher systems. Each launcher will have eight such missiles in two stacks and are launched in a canister configuration. The system is also fitted with an advanced radio frequency (RF) seeker.The Indian Army ordered five regiments of this version, which consists of about 40 launchers and 200 missiles for ₹17,000 crore(US$2.4 billion). It is expected to be deployed by 2023 with first deliveries commencing in 2020.LRSAM (Barak-8ER)It has been reported that an ER (extended range) variant of the Barak 8 is under development, which will see the missiles maximum range increased to 150 km.Designed to engage multiple beyond visual range threats, the low launch signature Barak-8ER is understood to retain the same autopilot/inertial navigation system and active radar seeker guidance as the Barak-8, although some modifications to the software and to the missile control surfaces are likely. The booster increases the length of the missile at launch from its current 4.5 m to nearly 6 m, although the length in flight after the booster has been jettisoned may be slightly less than the base Barak-8 missile, if a TVC is not present. The missile diameter and fin spans are thought to be the same as the base Barak-8. The booster weight is currently unknown, although the missile's weight after the booster has been jettisoned is the same as that for the current Barak-8 configuration.Levy said that initial operational capability (IOC) for Barak-8ER will first be declared for the naval variant, followed by IOC for the land variant. He declined to comment on a launch customer for Barak-8ER, but noted "existing Barak-8 customers will be interested in this configuration because it offers additional capability to their current system".The missile is expected to equip the Indian Navy's future Visakhapatnam-class destroyers.India has purchased new S-400 air defense system from Russia.S-400 missile systemThe S-400 Triumf is an anti-aircraft weapon system developed in the 1990s by Russia's Almaz Central Design Bureau as an upgrade of the S-300 family. It has been in service with the Russian Armed Forces since 2007. The S-400 uses four missiles to fill its performance envelope: the very-long-range 40N6 (400 km), the long-range 48N6 (250 km), the medium-range 9M96E2 (120 km) and the short-range 9M96E (40 km). The S-400 was described by The Economist in 2017 as "one of the best air-defence systems currently made".One system comprising up to 8 divisions (battalions) can control up to 72 launchers, with a maximum of 384 missiles(including missiles with a range of less than 250 km (160 mi)).The missiles are fired by a gas system from the launch tubes up to 30 metres into the air before the rocket motor ignites, which increases the maximum and decreases the minimum ranges.In April 2015, a successful test firing of the missile was conducted at an airborne target at a range of 400 km (250 mi);TELs carrying the long-range 40N6 may only be able to hold two missiles instead of the typical four due to its larger size.Another test recorded a 9M96 missile using an active radar homing head, signNowed a height of 56 km.All the missiles are equipped with directed explosion warhead, which increases the probability of complete destruction of targets.In 2016, Russian anti-aircraft missile troops received new guided missiles for S-300 and S-400 defense systems.Anti-aircraft missile system, designed to destroy aircraft, cruise and ballistic missiles, it can also be used against ground objectives.The S-400 is able to intercept cruise missiles out to a range of about 40 km due to their low altitude flight paths.On 15 October 2016 during the BRICS Summit, India and Russia signed an Inter-governmental Agreement (IGA) for the supply of five S-400 anti-aircraft missile systems.On 5 October 2018, India and Russia signed a US$5.43 billion (₹40,000CR) deal for five S-400 missile systems. The deliveries are expected to commence in 24 months, by the end of 2020.
-
Is it true that an e-assessment scheme for faceless scrutiny of income tax returns is notified?
E Assessment Scheme Notified by Income Tax Department for faceless Scrutiny.In exercise of the powers conferred by sub-section (3A) of section 143 of the Income-tax Act, 1961 (43 of 1961), the Central Government hereby makes the following Scheme, namely:–1. Short title and commencement.— (1) This Scheme may be called the E-assessment Scheme, 2019.(2) It shall come into force on the date of its publication in the Official Gazette.2. Definitions .— (1) In this Scheme, unless the context otherwise requires, —(i) “Act” means the Income-tax Act, 1961 (43 of 1961);(ii) “addressee” shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (b) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(iii) “assessment” means assessment of total income or loss of the assessee under sub-section (3) of section 143 of the Act;(iv) “authorised representative” shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in sub-section (2) of section 288 of the Act;(v) “automated allocation system” means an algorithm for randomised allocation of cases, by using suitable technological tools, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, with a view to optimise the use of resources;(vi) “automated examination tool” means an algorithm for standardised examination of draft orders, by using suitable technological tools, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, with a view to reduce the scope of discretion;(vii) “Board” means Central Board of Direct Taxes constituted under the Central Board of Revenues Act, 1963 (54 of 1963);(viii) “computer resource” shall have the same meaning as assigned to them in clause (k) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(ix) “computer system” shall have the same meaning as assigned to them in clause (1) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(x) “computer resource of assessee” shall include assessee’s registered account in designated portal of the Income-tax Department, the Mobile App linked to the registered mobile number of the assessee, or the email account of the assessee with his email service provider;(xi) “digital signature” shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (p) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(xii) “designated portal” means the web portal designated as such by the Principal Chief Commissioner or Principal Director General, in charge of the National e-assessment Centre;(xiii) “e-assessment” means the assessment proceedings conducted electronically in ‘e-Proceeding’ facility through assessee’s registered account in designated portal;(xiv) “electronic record” shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (t) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(xv) “electronic signature” shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (ta) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(xvi) “email” or “electronic mail” and “electronic mail message” means a message or information created or transmitted or received on a computer, computer system, computer resource or communication device including attachments in text, image, audio, video and any other electronic record, which may be transmitted with the message.;(xvii) “hash function” and “hash result” shall have the same meaning as assigned to them in the Explanation to sub-section (2) of section 3 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(xviii) “Mobile app” shall mean the application software of the Income-tax Department developed for mobile devices which is downloaded and installed on the registered mobile number of the assessee;(xix) “originator” shall have the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (za) of sub-section (1) of section 2 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000);(xx) “real time alert” means any communication sent to the assessee, by way of Short Messaging Service on his registered mobile number, or by way of update on his Mobile App, or by way of an email at his registered email address, so as to alert him regarding delivery of an electronic communication;(xxi) “registered account” of the assessee means the electronic filing account registered by the assessee in designated portal;(xxii) “registered e-mail address” means the e-mail address at which an electronic communication may be delivered or transmitted to the addressee, including‑(a) the email address available in the electronic filing account of the addressee registered in designated portal; or(b) the e-mail address available in the last income-tax return furnished by the addressee; or(c) the e-mail address available in the Permanent Account Number database relating to the addressee; or(d) in the case of addressee being an individual who possesses the Aadhaar number, the e-mail address of addressee available in the database of Unique Identification Authority of India ;or(e) in the case of addressee being a company, the e-mail address of the company as available on the official website of Ministry of Corporate Affairs; or(f) any e-mail address made available by the addressee to the income-tax authority or any person authorised by such authority.(xxiii) “registered mobile number” of the assessee means the mobile number of the assessee, or his authorised representative, appearing in the user profile of the electronic filing account registered by the assessee in designated portal;(xxiv) “video telephony” means the technological solutions for the reception and transmission of audio-video signals by users at different locations, for communication between people in real-time.(2) Words and expressions used herein and not defined but defined in the Act shall have the meaning respectively assigned to them in the Act.3. Scope of the Scheme.— The assessment under this Scheme shall be made in respect of such territorial area, or persons or class of persons, or incomes or class of incomes, or cases or class of cases, as may be specified by the Board.4. E-assessment Centres.— (1) For the purposes of this Scheme, the Board may set up‑(i) a National e-assessment Centre to facilitate the conduct of e-assessment proceedings in a centralised manner, which shall be vested with the jurisdiction to make assessment in accordance with the provisions of this Scheme;(ii) Regional e-assessment Centres as it may deem necessary to facilitate the conduct of e-assessment proceedings in the cadre controlling region of a Principal Chief Commissioner, which shall be vested with the jurisdiction to make assessment in accordance with the provisions of this Scheme;(iii) assessment units, as it may deem necessary to facilitate the conduct of e-assessment, to perform the function of making assessment, which includes identification of points or issues material for the determination of any liability (including refund) under the Act, seeking information or clarification on points or issues so identified, analysis of the material furnished by the assessee or any other person, and such other functions as may be required for the purposes of making assessment;(iv) verification units, as it may deem necessary to facilitate the conduct of e-assessment, to perform the function of verification, which includes enquiry, cross verification, examination of books of accounts, examination of witnesses and recording of statements, and such other functions as may be required for the purposes of verification.(v) technical units, as it may deem necessary to facilitate the conduct of e-assessment, to perform the function of providing technical assistance which includes any assistance or advice on legal, accounting, forensic, information technology, valuation, transfer pricing, data analytics, management or any other technical matter which may be required in a particular case or a class of cases, under this Scheme; and(vi) review units, as it may deem necessary to facilitate the conduct of e-assessment, to perform the function of review of the draft assessment order, which includes checking whether the relevant and material evidence has been brought on record, whether the relevant points of fact and law have been duly incorporated in the draft order, whether the issues on which addition or disallowance should be made have been discussed in the draft order, whether the applicable judicial decisions have been considered and dealt with in the draft order, checking for arithmetical correctness of modifications proposed, if any, and such other functions as may be required for the purposes of review,and specify their respective jurisdiction.(2) All communication among the assessment unit, review unit, verification unit or technical unit or with the assesse or any other person with respect to the information or documents or evidence or any other details, as may be necessary for the purposes of making an assessment under this Scheme shall be through the National e-assessment Centre.(3) The units referred to in sub-paragraphs (iii), (iv), (v) and (vi) of paragraph (1) shall have the following authorities, namely:—(a) Additional Commissioner or Additional Director or Joint Commissioner or Joint Director, as the case may be;(b) Deputy Commissioner or Deputy Director or Assistant Commissioner or Assistant Director, or Income-tax Officer, as the case may be;(c) such other income-tax authority, ministerial staff, executive or consultant, as considered necessary by the Board.5. Procedure for assessment.—(1) The assessment under this Scheme shall be made as per the following procedure, namely:—(i) the National e-Assessment Centre shall serve a notice on the assessee under sub-section (2) of section 143, specifying the issues for selection of his case for assessment;(ii) the assessee may, within fifteen days from the date of receipt of notice referred to in sub-clause (i), file his response to the National e-assessment Centre ;(iii) the National e-assessment Centre shall assign the case selected for the purposes of e-assessment under this Scheme to a specific assessment unit in any one Regional e-assessment Centre through an automated allocation system;(iv) where a case is assigned to the assessment unit, it may make a request to the National e-assessment Centre for(a) obtaining such further information, documents or evidence from the assesse or any other person, as it may specify;(b) conducting of certain enquiry or verification by verification unit; and(c) seeking technical assistance from the technical unit;(v) where a request for obtaining further information, documents or evidence from the assessee or any other person has been made by the assessment unit, the National e-assessment Centre shall issue appropriate notice or requisition to the assessee or any other person for obtaining the information, documents or evidence requisitioned by the assessment unit;(vi) where a request for conducting of certain enquiry or verification by the verification unit has been made by the assessment unit, the request shall be assigned by the National e-assessment Centre to a verification unit through an automated allocation system;(vii) where a request for seeking technical assistance from the technical unit has been made by the assessment unit, the request shall be assigned by the National e-assessment Centre to a technical unit in any one Regional e-assessment Centres through an automated allocation system;(viii) the assessment unit shall, after taking into account all the relevant material available on the record, make in writing, a draft assessment order either accepting the returned income of the assessee or modifying the returned income of the assesse, as the case may be, and send a copy of such order to the National e-assessment Centre;(ix) the assessment unit shall, while making draft assessment order, provide details of the penalty proceedings to be initiated therein, if any;(x) the National e-assessment Centre shall examine the draft assessment order in accordance with the risk management strategy specified by the Board, including by way of an automated examination tool, whereupon it may decide to(a) finalise the assessment as per the draft assessment order and serve a copy of such order and notice for initiating penalty proceedings, if any, to the assessee, alongwith the demand notice, specifying the sum payable by, or refund of any amount due to, the assessee on the basis of such assessment; or(b) provide an opportunity to the assessee, in case a modification is proposed, by serving a notice calling upon him to show cause as to why the assessment should not be completed as per the draft assessment order; or(c) assign the draft assessment order to a review unit in any one Regional e-assessment Centre, through an automated allocation system, for conducting review of such order;(xi) the review unit shall conduct review of the draft assessment order, referred to it by the National e-assessment Centre whereupon it may decide to(a) concur with the draft assessment order and intimate the National e-assessment Centre about such concurrence; or(b) suggest such modification, as it may deem fit, to the draft assessment order and send its suggestions to the National e-assessment Centre;(xii) the National e-assessment Centre shall, upon receiving concurrence of the review unit, follow the procedure laid down in sub-paragraph (a) or sub-paragraph (b) of paragraph (x), as the case may be;(xiii) the National e-assessment Centre shall, upon receiving suggestions for modifications from the review unit, communicate the same to the Assessment unit;(xiv) the assessment unit shall, after considering the modifications suggested by the Review unit, send the final draft assessment order to the National e-assessment Centre;(xv) The National e-assessment Centre shall, upon receiving final draft assessment order, follow the procedure laid down in sub-paragraph (a) or sub-paragraph (b) of paragraph (x),as the case may be;(xvi) The assessee may, in a case where show-cause notice under sub-paragraph (b) of paragraph (x) has been served upon him, furnish his response to the National e-assessment Centre on or before the date and time specified in the notice;(xvii) The National e-assessment Centre shall,-(a) in a case where no response to the show-cause notice is received, finalise the assessment as per the draft assessment order,as per the procedure laid down in sub-paragraph (a) of paragraph (x); or(b) in any other case, send the response received from the assessee to the assessment unit;(xviii) The assessment unit shall, after taking into account the response furnished by the assessee, make a revised draft assessment order and send it to the National e-assessment Centre;(xix) The National e-assessment Centre shall, upon receiving the revised draft assessment order,-(a) in case no modification prejudicial to the interest of the assessee is proposed with reference to the draft assessment order, finalise the assessment as per the procedure laid down in sub-paragraph (a) of paragraph (x); or(b) in case a modification prejudicial to the interest of the assessee is proposed with reference to the draft assessment order,provide an opportunity to the assessee, as per the procedure laid down in subparagraph (b) of paragraph (x);(c) the response furnished by the assessee shall be dealt with as per the procedure laid down in paragraphs (xvi),(xvii), and (xviii);(xx) The National e-assessment Centre shall, after completion of assessment, transfer all the electronic records of the case to the Assessing Officer having jurisdiction over such case., for —(a) imposition of penalty;(b) collection and recovery of demand;(c) rectification of mistake;(d) giving effect to appellate orders;(e) submission of remand report, or any other report to be furnished, or any representation to be made, or any record to be produced before the Commissioner (Appeals), Appellate Tribunal or Courts, as the case may be;(f) proposal seeking sanction for launch of prosecution and filing of complaint before the Court; Notwithstanding anything contained in paragraph (xx), the National e-assessment Centre may at any stage of the assessment, if considered necessary, transfer the case to the Assessing Officer having jurisdiction over such case.6. Penalty proceedings for non-compliance.— (1) Any unit may, in the course of assessment proceedings, for noncompliance of any notice, direction or order issued under this Scheme on the part of the assessee or any other person, send recommendation for initiation of any penalty proceedings under Chapter XXI of the Act, against such assesse or any other person, as the case may be, to the National e-assessment Centre, if it considers necessary or expedient to do so.(2) The National e-assessment Centre shall, on receipt of such recommendation, serve a notice on the assessee or any other person, as the case may be, calling upon him to show cause as to why penalty should not be imposed on him under the relevant provisions of the Act.(3) The response to show – cause notice furnished by the assessee or any other person, if any, shall be sent by the National e-assessment Centre to the concerned unit which has made the recommendation for penalty.(4) The said unit shall, after taking into consideration the response furnished by the assesse or any other person, as the case may be, –(a) make a draft order of penalty and send a copy of such draft to National e-assessment Centre; or(b) drop the penalty after recording reasons, under intimation to the National e-assessment Centre.(5) The National e-assessment Centre shall levy the penalty as per the said draft order of penalty and serve a copy of the same on the assessee or any other person, as the case may be.7. Appellate Proceedings.– An appeal against an assessment made by the National e-assessment Centre under this Scheme shall lie before the Commissioner (Appeals) having jurisdiction over the jurisdictional Assessing Officer and any reference to the Commissioner (Appeals) in any communication from the National e-assessment Centre shall mean such jurisdictional Commissioner (Appeals).8. Exchange of communication exclusively by electronic mode.— For the purposes of this Scheme,-(a) all communications between the National e-assessment Centre and the assessee, or his authorised representative, shall be exchanged exclusively by electronic mode; and(b) all internal communications between the National e-assessment Centre, Regional e-assessment Centres and various units shall be exchanged exclusively by electronic mode.9. Authentication of electronic record.— For the purposes of this Scheme, an electronic record shall be authenticated by the originator by affixing his digital signature in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (2) of section 3 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000):Provided that in case of the originator, being the assesse or any other person, such authentication may also be done by electronic signature or electronic authentication technique in accordance with the provisions of sub-section (2) of section 3A of the said Act:10. Delivery of electronic record.—(1) Every notice or order or any other electronic communication under this Scheme shall be delivered to the addressee, being the assessee, by way of‑(a) placing an authenticated copy thereof in the assessee’s registered account; or(b) sending an authenticated copy thereof to the registered email address of the assessee or his authorised representative; or(c) uploading an authenticated copy on the assessee’s Mobile App; andfollowed by a real time alert.(2) Every notice or order or any other electronic communication under this Scheme shall be delivered to the addressee, being any other person, by sending an authenticated copy thereof to the registered email address of such person, followed by a real time alert.(3) The Assessee shall file his response to any notice or order or any other electronic communication, under this Scheme, through his registered account, and once an acknowledgement is sent by the National e-assessment Centre containing the hash result generated upon successful submission of response, the response shall be deemed to be authenticated.(4) The time and place of dispatch and receipt of electronic record shall be determined in accordance with the provisions of section 13 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000).11. No personal appearance in the Centres or Units.—(1) A person shall not be required to appear either personally or through authorised representative in connection with any proceedings under this Scheme before the income-tax authority at the National e-assessment Centre or Regional e-assessment Centre or any unit set up under this Scheme.(2) In a case where a modification is proposed in the draft assessment order, and an opportunity is provided to the assessee by serving a notice calling upon him to show-cause as to why the assessment should not be completed as per the such draft assessment order, the assessee or his authorised representative, as the case may be, shall be entitled to seek personal hearing so as to make his oral submissions or present his case before the income-tax authority in any unit under this Scheme, and such hearing shall be conducted exclusively through video conferencing, including use of any telecommunication application software which supports video telephony, in accordance with the procedure laid down by the Board.(3) Any examination or recording of the statement of the assessee or any other person (other than statement recorded in the course of survey under section 133A of the Act) shall be conducted by an income-tax authority in any unit under this Scheme, exclusively through video conferencing, including use of any telecommunication application software which supports video telephony in accordance with the procedure laid down by the Board.(4) The Board shall establish suitable facilities for video conferencing including telecommunication application software which supports video telephony at such locations as may be necessary, so as to ensure that the assessee, or his authorised representative, or any other person referred to in sub-paragraph (2) or sub-paragraph (3) is not denied the benefit of this Scheme merely on the consideration that such assessee or his authorised representative, or any other person does not have access to video conferencing at his end.12. Power to specify format, mode, procedure and processes.—(1) The Principal Chief Commissioner or the Principal Director General, in charge of the National e-assessment Centre shall lay down the standards, procedures and processes for effective functioning of the National e-assessment Centre , Regional e-assessment Centres and the unit set-up under this Scheme, in an automated and mechanised environment, including format, mode, procedure and processes in respect of the following, namely:–(i) service of the notice, order or any other communication;(ii) receipt of any information or documents from the person in response to the notice, order or any other communication;(iii) issue of acknowledgment of the response furnished by the person;(iv) provision of “e-proceeding” facility including login account facility, tracking status of assessment, display of relevant details, and facility of download;(v) accessing, verification and authentication of information and response including documents submitted during the assessment proceedings;(vi) receipt, storage and retrieval of information or documents in a centralised manner;(vii) general administration and grievance redressal mechanism in the respective Centres and units.[Notification No. 61/2019/F.No. 370149/154/2019-TPL]ANKUR GOYAL, Under Secy.TO KNOW MORE : EXPERTMILE
Trusted esignature solution— what our customers are saying
be ready to get more
Get legally-binding signatures now!
Frequently asked questions
How do i add an electronic signature to a word document?
When a client enters information (such as a password) into the online form on , the information is encrypted so the client cannot see it. An authorized representative for the client, called a "Doe Representative," must enter the information into the "Signature" field to complete the signature.
How to use electronic signature paint?
Here is how to use electronic signature paint:
1. Get started in this tutorial, and follow all steps.
2. Take your digital signature and print it on a piece of paper, paper that is not too thick. You can use a regular paper for that. We recommend paper with the same color as your skin, as it will ensure that your signature will be easy to see. If your signature does not fit on your paper, it will be very difficult to see on it.
3. Get a paint marker. You would be surprised how much this costs, and for good reasons. We've found cheap paint markers at local craft shops. If you can't make these yourself, then get a good brand like Tacky or Wet N' Wild. You can buy these at local craft stores, or you can buy them online. We buy ours at , where it costs just $ for a ounce bottle.
4. After you've purchased and used a paint marker, take that paint marker to a surface that is not too slick for ink to adhere to, and lightly paint your digital signature onto it. This will not be too messy, and it is a good idea to paint lightly, since the thicker the paint, the more ink that will be needed.
5. Place your signature on the paper that you want your digital signature on, such as a piece of newspaper.
6. Using the tip of the paint marker, apply very light pressure to the paper with a very light stroke. The lighter your stroke, the harder it will be to see. You want it to be very lightly brushed, without the brush leaving any ink on the paper.
7. Remove the paper from the paper hol...
How to sign up for your congressional leaders e-newsletters?
Just click the links on this page below. Donate! If you want to donate to the Campaign for Liberty, your generous contribution can help us in our efforts to build a permanent grass roots movement for limited constitutional government. And it's easy to do — just click the button below!
Get more for Electronic signature Word for Administrative Mobile
- How To Electronic signature Tennessee Non disclosure agreement sample
- Can I Electronic signature Minnesota Mutual non-disclosure agreement
- Electronic signature Alabama Non-disclosure agreement PDF Safe
- Electronic signature Missouri Non-disclosure agreement PDF Myself
- How To Electronic signature New York Non-disclosure agreement PDF
- Electronic signature South Carolina Partnership agreements Online
- How Can I Electronic signature Florida Rental house lease agreement
- How Can I Electronic signature Texas Rental house lease agreement
Find out other Electronic signature Word for Administrative Mobile
- Mls waiver form
- Brokers opinion of value southeast bank properties form
- Noahs fmc form
- One step contractpdf form
- Selleramp39s mred exemption form
- Tar 1906 form
- Landlord quarterly inspection form
- Application and waiting list information
- Offer to rent form beava inc
- Va option clause form
- Clergy worksheet form
- Westside rentals application form 1232370
- Hopwa landlord participation agreement form
- Deposit to hold a lot on subdivision form
- General financed contract 061614docx form
- Tunic group form
- Bay area turning point auction item donation form
- First look appraisals appraisal rebuttal form
- House rental waiver form
- Escrow disbursement authorization form rev 2016 excel realty