Parallel Signature Block Routing Made Easy
Do more online with a globally-trusted eSignature platform
Standout signing experience
Trusted reporting and analytics
Mobile eSigning in person and remotely
Industry rules and compliance
Parallel signature block routing, quicker than ever
Helpful eSignature add-ons
See airSlate SignNow eSignatures in action
airSlate SignNow solutions for better efficiency
Our user reviews speak for themselves






Why choose airSlate SignNow
-
Free 7-day trial. Choose the plan you need and try it risk-free.
-
Honest pricing for full-featured plans. airSlate SignNow offers subscription plans with no overages or hidden fees at renewal.
-
Enterprise-grade security. airSlate SignNow helps you comply with global security standards.

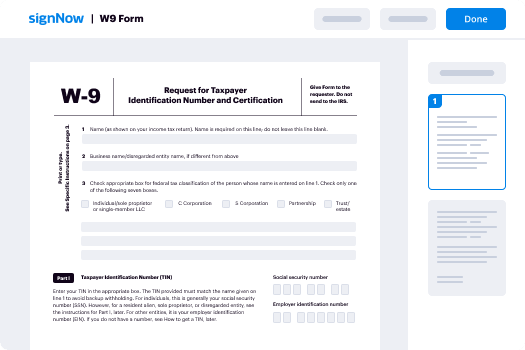
Your step-by-step guide — parallel signature block routing
Leveraging airSlate SignNow’s electronic signature any organization can accelerate signature workflows and sign online in real-time, delivering a greater experience to customers and employees. Use parallel signature block Routing in a few simple actions. Our handheld mobile apps make work on the go possible, even while off-line! Sign documents from any place in the world and complete tasks quicker.
Follow the stepwise guide for using parallel signature block Routing:
- Sign in to your airSlate SignNow account.
- Find your record within your folders or import a new one.
- Open the document adjust using the Tools menu.
- Place fillable areas, type text and eSign it.
- Add several signers by emails and set up the signing sequence.
- Specify which users will receive an executed copy.
- Use Advanced Options to limit access to the document and set an expiration date.
- Press Save and Close when done.
Additionally, there are more advanced functions available for parallel signature block Routing. Include users to your common workspace, view teams, and monitor collaboration. Numerous users all over the US and Europe concur that a system that brings people together in one unified digital location, is exactly what businesses need to keep workflows performing smoothly. The airSlate SignNow REST API enables you to integrate eSignatures into your application, internet site, CRM or cloud storage. Try out airSlate SignNow and enjoy quicker, smoother and overall more efficient eSignature workflows!
How it works
airSlate SignNow features that users love
See exceptional results parallel signature block Routing made easy
Get legally-binding signatures now!
What active users are saying — parallel signature block routing
Related searches to parallel signature block Routing made easy
Parallel signature block routing
hi guys so I am going to start so I hope maximum people have joined so whosoever has to join they can join I hope you are able to hear me you can type on chat if you guys are able to hear me you can't IPS so that I can start yes I can hear it hi that Malia okay that's fine so I will give a brief introduction about myself I am Santosh Sharma and I am from DRS intercom I provide online training and this is my website you can check the course here and you can also follow subscribe my youtube channel I am also recording this video so I will upload this in my youtube channel and probably you can get it once I will upload it so let's start this is what I will cover today so this I have also shared in the chat so I will try to cover maximum topics or almost all the topics if time will allow so here I will discuss about the parallel to firewall only I will not try to compare with other firewalls but wherever it would be required than I'll do so parallel to firewall it was founded in 2005 by a teacher I am just giving you a basic introduction from the starting who are pressure they can have some idea so net Juke has founded this parallel to firewall in 2005 and in 2007 he just in he came up with his firewall and there were some great features which he has given in his firewall and it just thrilled the market because at the time market was not having such a great awesome technology like app ID identification currently maximum pharaohs are having mechanism that the Pharaoh can identify the application very well like if you heard about a firewall named photogate that is also comes under the leader its YouTube feature is very perfect but if you talk about 2007 that was really also featured which came into the market at the time and content ID inspection tilde this is really awesome feature we will discuss this in detail how it is different from other vendors so there is one thing you might have heard sp3 single pass parallel processing this is something was new in the parallel toe and all these three things are nice please do not allow do not enable your video okay so this is giving me kind of distraction so this was these all three things were patented by the parallel dough to understand what is what is single passed parallel processing we should be aware that what is multi pass architecture so in multi pass what was happening your packet will come and it will get processed by the firewall policy they will get checked at the layer three layer for policy and then layer two layer three functionality will be performed at the last if you have enabled you Jim features then what will happen your URL filtering your ideas your antivirus will get checked but all those having different database so if they are having different Attaway so what will happen the packet will go down get checked and again this thing will happen you can see this thing is happening again and again it is passing multiple time so what is happening performance is degrading so performance is degrading because it has to check multiple time multiple time your packet is passing so this is multi pass architecture so parallel to came with single pass parallel processing so I hope you understood what is multi pass I will take an example suppose you are going to a mall and there you have a box you have your suitcase and your in your suitcase there is one lunch box and your clothes and there is some your beauty items so there are different guards to check different things you will open your lunch box you will check if there is like no Boyson in that maybe you go to the mall then you can offer that to someone he will check your clothes and you will check so there if there should not be something bad written in your clothes like that can give other people a bad impression so he will check your beauty items or something he will check there should not be a knife or something like that that you can harm somebody else so they all are doing their job perfectly fine they are checking you in all the specs you should you should not be carrying something dangerous so what is happening your time is also getting wasted and your resources are also getting applies multiple resources so that is multipaths that was an example of multi pass so here performance is getting degraded now we can discuss about what a single boss so single pass parallel processing these two are two different terminologies and technology we cannot combine them so we have to understand them very separately single pass means your packet is passing singly one time only parallel processing is parallel processing of your hardware it is not like that if your packet is coming inside and at the same time it is going here here here that is not happening here this is not a parallel processing that can be a parallel processing like a single packet which is again wastage if you are sending a packet at three different places same time that is again wastage you are multiplying a packet and again source is in fact utilized processing hardware means your hardware is doing parallel processing so how it is doing I will explain you so this is I have taken example of one machine so what happens when you go to burst and when you go to airport again this is a real-life example you put your suitcase here and your suitcase past one time is this single pass it is not like that it has to open your suitcase and half it has to check what are the items here and it is not like that there are different machines to check that it will go once checked once and then you will carry and you can do but all the items are put in these series only okay one by one they will go one another one that will per now what is parallel processing that is parallel processing hardware now you can see you have multiple hardware okay so if four person will come they can put their suitcase and their suitcase will get processed at the same time okay this is called parallel processing now how we can apply this in our parallel to firewall I will take you there so single pass single pass is always applied in your content ID Content ID is where your unified engine is their common signatures are their means their content is processed only once how it is processed once I will explain you these are just little things which I am explaining performance remains steady your performance will not be changed so what happens there are two type of techniques to inspect something one is slow raise another is stream-based Flo is and Clovis sorry one is stream-based and another is proxy based flow based name is in putting it stream based and profits are the same proxy based are like you have given your item and your item suppose you have seven boxes your seven boxes will be buffered and they will check one where one another example I can take suppose you are going along with your family to a mall then you all the person will come one by one from the gate you all will come and you have to gather somewhere and you all will be checked together but stream base is that once one will go that will check at that time there is no buffering same as imperil dope packet will come into the firewall that will get processed that will get scanned and that will go forward if you are downloading one GB file that file will be checked in chunks it is not like that file has to buffer that it will be checked in flow but in proxy base Perl has to download whole file it has to check after downloading it has to inspect so this what is happening your performance will degrade in proxy based putting it like I am talking about other vendor that is supporting proxy base and stream based also but Palo Alto is only having stream based malware scanning so that is the reason it is so much past performance is good another example this is this is what they are doing how packet is passing only single time there is only one pattern database there are no different databases like we have seen in our existing diagram if you have one level one nobility scanning if you want to check for malware matches if you want to check for botnet pile type matches like your data card sorry your credit card okay and data match is like DLP if you talk about data loss mention if you are updating any adult file so there is only one single database where your file will get checked here everything will happen here okay there is no nothing like that your packet once come it has to go by different databases there is only one database larroquette check scan it all scan it once it will scan everything whatever profile will be applied and we'll check on it once there is another database which is URL filtering database so there are 1 million URL database we can create like custom URL we can create and 180 million URL that is already exists and keep on increasing day by day so this is the hardware of hardware diagram of palo alto it's divided into two parts one is control plane and other is data plane in control planes you can see there are dual CPU there are different ramps holidays in data plane also there are it is divided into three parts there are three different processors in control plane as the name is saying that it is for controlling the fire role like you want to manage the fire role and extra control plane if you want to process your data data means your internet data if you want to access internet or you want to talk with someone then that is data plane where your knotting functionality will happen that is natural processor security processor is harder in turn I will not go into the detail of that but my purpose of saying is you can see there are multiple hardware so the parallel sp3 a lot harder processing what I was saying so there are multiple hardware's are there that's what what they are doing multiple time they are processing the your packet okay so this is the second example this is a big hardware you can see now the cores are more okay Ram is also increased it depends how much money you are spending now you can see there are three engines okay ranging for SSL IPSec and their signature matching also there are different engines and data plane is a big big twenty Gbps of speed processor is there so it depends upon how much money you are spending and this whole slide is only on understanding single pass parallel processing so again another example to give you an idea what is that earlier what happens one packet is for your accessing your firewall so obviously that will go to your control plan that all packet will be saved in DCP buffer this is CP buffer that will be buffered okay why they are buffered because there is a one common CPU okay and comments if you would be having common CP buffer one way one packet will go okay you can see the packets are going in series their process in series why because we have only one common CP work but in case of powerto we have now multiple cores okay now packet will come you can see access firewall and internet access packets are coming they will get processed in different cores and they will perrolli their process this is called parallel processing here is another example we are going into detail now this is taken from the data plane earlier that was only single data plane where the Packers were handling and we can go in detail but packet is coming it's going to the data plane and again here it is divided into its different engines and in different engines you can see there are different CPUs if you one if you two okay and it will get processed from and it will go to the signature match and again family it will go to the Egret so you can see the whole process is happening parallel so this is what parallel harder processing so hardware is doing a parallel processing otherwise your packets are coming in series one after another your packet will come okay but they are getting processed perrolli one kosher might come in your mind like there are different CPUs so how these CPUs are handling packets like who will handle the packet force if you wants if you do how this is being handled so there is again a very good load load balancing which is happening in CPU level there is one CPU which is called master and cannabis abuse it will be working under the master packet will come if new UDP connection packet came it will distribute to one of the CPU which is free if another UDP comes it will distribute to another if TCP comes then it will distribute to another so here the thing is that new TCP connection and new UDP connections will be handled by the other CPUs and that will be given by the CPU master it will work as the manager like there is a manager in our office he work comes to him then he distribute the work to all the members same thing happens here there is a one CPU which acts as a master and it distributes three packets what kind of packets and distributes new UDP and new TCP so the question comes what kind of packet CPU master does is have seen that I was explaining this any please comment on chat that you have hello are you able to hear me so have you seen up to here master computer Master Chief you okay you guys are really very sorry but I have recorded the video so I will I will upload that after that so maybe once again connection get disconnected I will join again because there is some fluctuation happening today of the light so one more time it may happen so I was talking about TDR CPUs one master CPU is there and there are some other CPUs which will work under thee master CPU so that is like a manager who is handing the work to other pieces and other CPUs new UDV connections will get handled by the other CPU and new TCP connection but there are some high level tasks which are handled by the master CPU which is new TCP non TCP UDP means TCP UDP will be handled by other but if there is some packet which is non TCP UDP that will be handled by your master PACA days IPSec packet will be handled by the master okay so this is I have written only if it will get is connected so you beyond that you meeting I will connect myself okay so I hope you understood what is single pass parallel processing as we have seen our diagram so packets are parallel oppressing is going parallel E another example I can give you suppose there is one hospital and there is only one doctor sitting that doctor will take care of ear nose eyes he will take care of everything okay so what will happen there will be a line of patients they have to wait so the same thing is happening CPU buffer your packets has to wait now we have a big Hospital like a Madonna and there are different doctors and different doctors are four different specialization one is for ear one is for nose eyes there are different doctors even there there are multiple doctors for same thing like different ports ok now what will happen there will be very less amount of buffering of patients patient can go to different doctors so so this is what happening here the parallely your patients processed they have no need to wait so this is work called parallel processing move on to the packet flow this is the detailed packet flow which I will explain you today some people really afraid of that and so in ten minutes my meeting will just end so I will connect again so you guys can connect again a big question if this is your firewall and your packet is received in the lam this is LAN and this is when okay so this is that and this is when and wherever your packet is received that is called ingress a packet is coming at LAN in LAN interface it is ingress a packet is coming from outside then this is called ingress okay so it is not like that English can be LAN or van it can be anything barrier packet is coming so suppose your packet is received and your packet sorry I think someone has have something okay so ingress in cases where your packet will hit so your packet once your packet hit to your firewall what will happen once your packet is hit by a firewall your fire was just captures some of the information so what that information is it will extract layer 3 and layer 4 information you can see here so this is what explained in this first step it will extract layer 2 layer 3 and layer information so what are the information of layer 2 layer 3 and therefore near to MAC address you know obviously layer 3 source IP of that system who is accessing google.com suppose source IP will be T IP address off the system destination IP will also go this will be IP of your google.com ok then what will grow in grace John why because it has hit your ingress interface and guess interface will also be the source to destination port so these all information will be gathered here if you have interface information like English interface you have it has hit to LAN interface obviously this is a John based firewall from there you can come to know okay which Joe on this interface is part so these information are gathered in this step once the packet is received so this is very very vital information that information will be used in next coming steps once your packet will go it will get processed obviously this is a firewall firewall inspection will happen your packet can also be discarded if there are some errors so I am not touching this it will be there obviously it will get discarded packet is like you said no other changes will happen it will go again and it will get decrypted after decrypted it will again capture layer 3 layer 4 information so for the time being you can just forget your packet is not IPSec you have a simple packet it came from ingress it just extracted layer 2 layer 2 information and there is no error it is getting a packet and now there is the most important thing one is fast path and one is slow bug you need to remember these things your packet needs to enter into fast path of the bush there are certain decisions which you have to be taken I will close this [Music] interesting Bible fast paths and fast it will check this session it will do the session the bugs in session hook up it will find if their packet some other tasks so the target came it went to the fast path and in fast path it will check the session table suppose session is not formed if the packet is the first packet obviously it's the first packet and packet will not be found in this session so it will go slow path engine in slow path it will perform some of them tasks like it will do forwarding lookup that we will discuss in the next of the contacted when it will come it will go to the fast path and their session will be found and it will be get processed in the fast path only ok so this I explained that first packet will go by the slow path only because session will not be found and the second packet or the subsequent packet will follow the fast path because they will get these session Alex I will show you how they will see the session so this is the choice I seen come on I have run I just entered the google.com so this is the destination this is the source this information is already having source for sport this is source IP this is source port destination IP this is destination port so shown destination zone where it has to NAT it and what is the translated IP okay so it also identifies the application so this is the session table we I have just entered through session all so here it has all the information if it is not having information here and it will go to the slow path in slow path how your packet is processing your packet will come to your slow path and here there are some of the steps it has to do first for review pub this is very important step and this is also useful in your troubleshooting you have or the packet flow you have to understand it because it will be helpful in troubleshooting as well all your security policies everything will be done by the packet flow only first forwarding look up it will find the egress zone forwarding means it has to forward the packet and where it has to understand where is egress Joan egress interface so your packet will come and there are certain things which it has to take care it depends upon how your firewall is configured is it configured into tap mode so what is tap mode tap mode is where your traffic is getting inspected okay like there is a tap and traffic is going one where one suppose there is one firewall and there is one fire I'll take one scenario there is a one codec eight firewall okay and existing users are able to access there it's going very fine they are happy now you are a parallel to engineer you went to this organization and you said your your photogate firewall is not working properly when the traffic is exiting your gran interface your some of the applications are allowed so they will say no we are able to see everything is blocked but they are saying this is photogate that's why you are able to see everything here but work if we you can give us one port as your tap port and we will deploy our parallel to firewall here and we want one copy of your traffic here and we will see the data and from here we will come to know what are the applications which your file is not blocking so this is called tap forward so what is happening in tap code there is only one interface which is getting the traffic it is inspecting expecting the traffic and it's exchange is all this drop it will not perform any action on that and just monitor the traffic so if your firewall is configured in attack mode then your egress interface is equal to ingress in interface where your packet is hit that is only the egress interface and action will always be proper if it is a V wiremold what will happen the milk I will work as transparent firewall suppose this is Ethernet 1/1 and this is Ethernet 1/2 table is a wire and there might be another router ok so if this is 1.1 IP 1 and is 192 168 1 dot 1 IP this a 1 and his two IP and if you will compare email or firewall in V wire more they will still be able to ping each other and they will not get any next row means it is transparently added into your network why I am telling you this because we have to understand where is our egress interface so in rewire we our self define our in this interface means our peer interface is always our egress in Turkish so if the packet will come to your fever your egress is equal to the peer interface it will if it will again get disconnected so only one minute is remained I will connect again you guys can also connect all of the guys can go on mute as there is some disturbance so I will just close this meeting I will get closed automatically so one person has asked what is the difference between John based firewall and what is difference between what I think you can hear me so I'll explain only one point about zone based firewall and interface based firewall because this is not our scope of discussion today the difference between interface like photogate file is interface based firewall so what happens there you can give your policy from land to when you can you can define one interface but in zone based in zone you can define multiple interfaces like you can define two interfaces and when you are applying the policy there is one policy that can work we are no need to create two different policies like example there is two different ISP sp1 and ISP - okay then there is a one van John in Van Jones you can call these two interfaces okay and you have to create policy one policy from land to - when so it will automatically take decision that it has to send - I see one or ISP - how it will take decision it will check your routing table it will make decision from there where it has to send so this is one one good scenario where we can say that what is different print shown and interface okay so we were discussing that what is we were so in vir I'll show you if you go to your firewall you there is virtual wire option and in virtual wire you can just give your interfaces so first interface will act as an ingress interface the second one is egress interface so the peer interface will be your egress interface so it is defined by yourself so that is what it's saying here if it is a V wire then here interface is the your egress interface from there it will come to know where it has to forward the packet but if it is layer 2 how it will come to know there is a MAC address and to search the MAC address and if it is not found it will do the broadcasting you you guys you will get the recording so you are joining late so definitely I will share in the recording with you okay so if you have missed something you will get covered from there so when the packet is coming to layer three how it will make the decision 90 percent firewalls are configured in your layer three mode only okay so if the packet will come to your layer three how it will make the decision it will make whenever I am asking questions you can type on chat also that will also give you understanding that do you have knowledge of that or not okay if a packet is coming for layer three it will check your route it will do the route lookup and from there it will find the next row so from here it will come to know what is the ingress job okay if there is no route it will discard the packet and then finally it will go for the NAD look up in that look up if you can type on the chat how many types of NAT are there when the packet will go to the netting you can see here if destination that is present then do second forwarding lookup so this was first forwarding lookup and this is second forwarding lookup happening here in the destination at something can ask you question which NAT is happening first so destination act is performed first and then source that happens okay if your firewall finds destination nak then your second firewall second folding lookup will happen now the question is that why second forwarding lookup will happen if it will find the destination back now let's take an example this is your fireball okay this is your band interface this is your DMZ interface and here is your server and your server is having IP address of 192 168 1 or 1 you got requirement today that application engineers are having server with this IP address and they are saying that to be one outside people to access our server so in that case you need to create destination at obviously okay so you have one free IP for an example we can take to door to door to this is our free IP and to row to row to series is which we are using outside dot zero okay now you have to make the netting how you will make the netting so what is your source into this your source interface is your ban interface because from outside people are coming to access your server which is placed here okay so your source interface will be an interface your source IP will be any and what is your destination interface you guys can type on chat what would be your destination interface you okay DMZ so it's very good that you told DMZ that that's why I am explaining here so DMZ would not be your destination interface reason for that is people are accessing your public IP okay they are not aware that what is the private IP private I've is in your DMZ but public IP is towards outside so you're nodding will be performed for your original packet your original packet is received like source is received in the van interface source and anybody can access what anybody can exist our to door to door to door to they can access to door to door - okay so - row 2.2 is in which interface side obviously public eye peas are outside our van interface so this is how your NAND policy will become okay this is original packet when you are making nad policy this is the only thing where people make the mistake rest of the thing are very easy Alex I'll show you here also let's go to the netting will create the net policy okay I'll delete this all I'll charge my laptop wait a second so here I'll make the policy you name you can give any name so shown so here your packet is received at the source side this will be Bank okay destination zone okay we'll talk about destination zone source are any because they are coming from outside anybody can access our server what is the IP address of our server who door-to-door you go to PI because they are not aware of private IP from outside we cannot access private IP when you are accessing your mobile dot mobile from your mobile you are opening google.com you are not aware what is the private IP of Google so here we need a destination address which is public so this is public IP address okay source addresses will be any so what would be the destination zone now you can have an idea from here only destination - Row 2 Row 2 is towards outside okay because your packet he just hit to your interface it came to your outside interference is this address is lying on outside so this is original packet so this is very important people are not able to understand about original packet you have to give your like will lose concentration here translated packet is very easy this is not difficult if you are doing source netting you can select the source netting if you are doing destination netting you just need to add the IP address of your original server for 92 168 1.1 for an example ok just click ok your NAT policy is done you if you have to create the security policy how you will create the security policy you best nation zone in Natick will not be DMZ the reason I have already told you the reason is that this yet you're netting is not happened okay you're netting not happen it means it is see see the packet flow game came and what it does it just done the forwarding lookup it done the forwarding lookup we will return the forwarding lookup and from where it came to know that packet came from Van interface and the destination is to Row 2 Row 2 it will find the route for to Row 2 Row 2 when it found a route for to Row 2 Row 2 it came to know that it is towards outside it is toward man obviously public IP will be towards man that's why destination interface is your man correct so then it went to the NAD and it came to know okay netting is happening and that is destination that what is happening now it has to find it has to do the lookup again okay so we were here sorry I was just finding out my slide so your packet is received your packet is received outside ran interface towards man interface when packet received at the van interface as I told you in the starting of the slide it will capture layer two layer three all this information when it captured the source IP it is any anything you can take one two three 1.1.1 when it captured the destination IP it came to know okay destination IP to Rho 2 Rho 2 Rho 2 something like their destination port and all those it captured it done forwarding lookup for destination when it done the forwarding blue curve for the destination it came to know this destination is towards van ok when it done it done ok it's towards friend now it will go for the next step here it's a layer 3 it done lookup it from that destination to Row 2 is towards man so that's why we typed the van over there now it found that packet is having destination Natick ok destination netting now I'll go to the firewall okay you can see here this is very important step that's why I am taking more time here okay so I think we have not clicked yes on that and not able to see okay this one so this is your original packet that's what I am typing here I am NOT doing any netting in original packet okay the original packet is van and this is what you are accessing destination okay this destination is towards your DMZ your firewall you are aware that it sorry it's it's sorry I type the engineer HP van it your destination zone is then why because your destination is towards here and how your fire will come to know that your destination is towards fan because it will do forwarding lookup okay it will do forwarding look up from there it came to know now when it seems to translate the packet it came to know oh it is destination nothing happening and when it is destination adding happening your destination IP address is changed from original IP a little to now it has changed now firewall is worried it has to do the forwarding look up again why it has to do because your destination has changed now your destination has changed it has to yeah you hello guys are you able to hear me so that I have selected DMZ there but it is not DMZ ladies are you able to hear me you hello okay yeah yes someone typed that that was the van interface obviously that was ran into bills maybe mistakenly I just typed DMZ so your packet is received very original packet is received that will be seen by your forwarding look of decision like route will be checked and it will come to know okay this is towards LAN interface so this is original packet here in NAT policy up to here up to regional packet no netting is done okay NAT is not performed here we have defined only original packet then it will go to the trans translate the packet here what we need to define we have defined to the destination adding so it will do the destination adding when you will do destination adding in the NAT step NAT lookup it from Dina and here once the dinette is found it will do second forwarding lookup now tell me after doing second forwarding lookup what would be our destination John can you type one correct now it will be DMZ because it will find the route it will find the route in the routing table and it will see that 192 168 1.1 is towards DMZ okay so now we have to create the security policy these are only two things where people are not able to understand what we need to do okay so now we have to create this security policy now now you will tell me what I have to do okay we'll be the source type in the chat you source zone source will source address will be any that's perfect source zone will be fanzone correct and what will be the destination zone that's missing drawn now will be your DMZ zone why because it has done deal look up it has done second forwarding look up okay from where we came to know that final packet will reside on your DMZ okay and what will be your destination address public address or private address here again there is some logic it will be your tutor tutor - I know some people are confused ok it will be tutor tutor - again why - Row 2 to 2 because here your security policies and nad policies are just look up look up is happening only ok netting and security policies are not getting applied mad policy will get applied in your fast path do not if applicable ok security policy is also just look up is happening policy look up so these lookups are before your packet get netted to door to door - will get nutty - 192 168 1 . 1 after it will go for checking the policy ok when the net will get applied here it just look up so it it is not naked yet that's why only to toe to toe to come will come your John will be different the reason for that this is destination nag and policy will be should be therefore where your packet is going to lie so if you compare what is the difference between NAT policy and the security policy only one difference your destination zone is getting changed destination zone will get changed from van to TMZ your destination is not getting changed the reason for that is this is prenatal policy okay your NAT will happen here do not decoupling ever your net is not happened that's why your public IP is not changed okay you're forwarding lookup happen your second forwarding lookup happened that's why it came from Grande to DMZ that is the reason okay I hope you understood that the reason for DMZ is only that your second forwarding lookup happened your second forwarding look of happened and from there it came to know that original destination is DMZ okay your IP is not getting IP is not 100 168 the reason for that your NAT will happen here not here that's why before applying that it need to check the security look up need to do the security policy look up that is the only reason suppose even if you are not able to understand that logic and you want to remember it there is only one difference you need to change the destination John destination John will be where the original packet will life okay when the server will reply to that that will be a stateful inspection there will be a session table okay session table will be there so it will check the table and it will automatically go from the same policy there is no like you have to create another policy or something like that these firewalls are stateful firewalls okay we have no need to create another policy for that only one policy will work okay so I hope this is clear and it will go to check your security policy your security policies masked and ruled match action allow then it will create each session if it is not match the policy it will discard the packet once the session is created that will go into layer two and layer four packet processing and this is what I explained in the starting next subsequent packets will follow fast path but this is first packet so this will go from slow path to fast path and here it will do nad if applicable it will do the netting if netting is applicable and then further it will do the SSL decryption so decryption is like if you want to open a packet if you want to suppose there is one chocolate and you want to see if there is a chocolate inside it or there is a soap okay so there is a soap and it is colored chocolate so you want to unwrap it then you will check if it is chocolate or not so that is what decryption does decryption just unwrap the packet it open the packet so this policy depends upon country to country some countries allows that some country doesn't allow it is not like that we can go on and just apply this if it is not loud it will go and check this session I've identified so where it will check if you see here your session table there is application already identified web browsing Google update this is I have created custom application test ok undecided like it is not able to identify the traffic ok so here it is maintaining this session for the application as a so this is what explained here okay you so okay it's the slide so here only the different part difficult part is here where you have to struggle you need to give your attention here ok the rest of the thing which are very simple now your packet will get checked for session application ok obviously this is the first package so session app will not be identified and it will go for identification it will identify the application here in application identification there are certain processes like app override what is the app override you can type in check what do you understand with Apple right so I will explain you what is a power I'd have over it suppose you have your application in DMZ and there is obviously there would not be any signature for that okay so whenever the packet will come it will do all the processing and it will reach here up to session AB and from here it will go to identify the application then it will identify the application obviously in spectrum based application identification this is a lot of database they would not be having any database for your personal application when it will go on checking it will say that I am NOT able to find out the application ok when it is not able to find out the application it will show you something like that undecided are unknown application not from something like that you will get in the application so what is this advantage of that this advantage of that when the second another packet will come that will ask session have identified then it will say no not identify unidentified then it will again check the application so how many time your packet will come it will keep on checking your application so your processing is happening all the time your CPU your extra resources are getting utilized so this is the option where you can override the application you can make custom signature and you can give it name this is test name I given and you can see that it is it has identified you can give your applications name whatever you like and you can add in your application and it will identify this and you can see it believes you and it just kept its pattern matching it believes in you and it will directly go you to you will directly go to security policy look up based on application if you have said that that application should be allowed it will go for the content inspection here otherwise it will get discarded ok suppose your negation is allowed and it will go for Content ID inspection let's discuss that this is a very detailed topic okay so I'm not explaining much here here where your SP 3 parallel single pass parallel processing you can say is happening your you have one database ok one single database where your all the features your antivirus your 5 year your vulnerability ok your IPS ideas all these things will get checked here and there is only one database the examples which I have given you in the starting there's only one database there it will get checked another thing very important thing is that application changed from content inspection ok if your application will get changed for example you are accessing facebook.com and in facebook.com you are going to access your chat also so your application has changed okay so it will check application changed again your application will go and it will identify there is no security policy for that then it will drop the packet so you cannot access the chat so this is very smart firewall where it will check if application is changed and there is any policy for that or not okay detection rules whatever is detected and after that it apply these security profiles and packet will be forwarded to your egress so this was our packet flow we'll go to our slide you you you okay so I think I have covered everything rhesus is just a virtual virtual system like if you have worked in photogate so like photogate can putting it there is a we don't in here the Palo Alto we say visas visas is just you are dividing your firewall into multiple instances like you have taken a big hardware of your firewall and now you need second firewall also you can divide your firewall you can you can make different instances of one firewall so once you divide that firewall there will be different CPU different RAM different memory for that firewall ok and that will work as individual fiber this is helpful like you do not have space or your you want to like save your space you have one firewall you want to save your money we don't want to purchase another another hard hardware but in your existing hardware there is capacity that you can divide that ok so you can utilize there is a veces so that is that is different vertical I can say a very advanced thing so this is what we see is ok so guys I have covered everything I hope there is seven minutes left I will just check your knowledge of Newton at ok what you turn at is I will see if I have captured any in diagram for that you mm-hmm okay there is there isn't any diagram and I will explain you there is one system okay this is your firewall and this is Van interface this is TMZ this is TMZ server and the IP address of TMZ is 172 168 1.1 this is 10.10 dot dot 10 okay and this is LAN van is having to door to door to door to okay so we can also make a policy from land to DMZ directly so that it wants to access the DMZ it can directly access but for security reason I want it has to go outside and then it has to access my DMZ okay this is you turn you can see this is you turn it is taking okay so they will when they have to access this URL that that will be W double dot s calm so that URL will get resolved into the public IP to door to door to door to okay so that for this destination will be to door to door to door to not this one so this is called u-turn at means even it has to do it has to exit GM did it will go outside and then it will come in that will be your new Turner so if I talk about the nat policy net policy is always for your original packet so what will be your source Joan and IP please type you perfect source zone will be LAN okay source zone will be land and IP will be 10.10 dot dot ten okay but will be your destination zone and IP correct this person is very much intelligent current Kapoor so destination John will be van and your destination IP will be 2 Rho 2 Rho 2 the reason behind is your destination is 2 root 2 root 2 it is getting resolved to 2.2 Road - okay the first thing that you have to type is destination okay if you are not able to understand the John you type the destination okay and then you think that the forwarding look look up the route will be rare rod will obviously be towards where not towards the DM debt for this IP address that is why your destination zone will be is so when you are creating the NAT policy the toughest part is you have to write original packet translated packet is very simple like you have to do the destination translation and there you need to type only 172 one sixth year 1.1 okay and what is what would be the security policy source John and IP source Sean will be land okay yeah Akhil - sorry yeah laughs and then I pee okay correct tender tender okay and what will be the destination John an IP perfect destination John will be third TMZ why DMZ because when it done the dirt when it done the NAD in nad it came to know that to door to door to is getting nati to 172 168 1.1 here we have found only the destination John but we have not done any netting so your destination IP will be to door to door to door warning perfect guys so this was today's class I hope you enjoyed you can give your comments you can just subscribe my channel ok I have I have mentioned in the chatting and you can I will also type here del dot youtube.com ok you can go here I will upload my video you can subscribe the channel and you can give comments if you like ok and there is my website if you want to see full content whatever classes we give you can see these labels here there are some more detailed packet to also where we tell you in the will you tell in the CLI so you can go here and you can check if you like you can contact us ok so ok you can just send me email if you have any doubt ok I will type my email here you ss one nine eight nine three nine add the red team Elcom you can type here and you can send your queries hope you guys bye you recording as I told you that recording I will upload so you can get the recording from there in YouTube so I told you that you can subscribe the channel and you can get the recording there ok TPT I cannot share because there is so much hard-working Peabody it took a lot of time for me when I had this created it took four hours so Peabody I cannot say okay but obviously recording I will share you oh you guys thanks bye have a nice day thanks thanks Danny thank you so much for each session even trading final bro that was the only class that that class was just to tell you about my method like how I teach you if you like the method then you can come for the paid classes so that was some much that I have explained here if anybody wish they can come for debate classes that's what like if you are spending money in different tutor and the method is not good then you're wasting your money but here you are investing your money what I think if you like like the class Thanks the class is always online class so we give you the troubleshooting and all those things so if you want a detailed discussion then you can count
Show more