Validate Electronic signature Word Secure
Make the most out of your eSignature workflows with airSlate SignNow
Extensive suite of eSignature tools
Robust integration and API capabilities
Advanced security and compliance
Various collaboration tools
Enjoyable and stress-free signing experience
Extensive support
Keep your eSignature workflows on track
Our user reviews speak for themselves






Grasping the concept of signature validation with airSlate SignNow
In the modern digital landscape, signature validation is crucial for confirming the authenticity and integrity of documents. airSlate SignNow streamlines this process, allowing users to safely transmit and sign documents effortlessly. Let's delve into the advantages of this platform and how to initiate its signature validation functionalities.
Procedure for signature validation using airSlate SignNow
- Access the airSlate SignNow website in your chosen browser.
- Create a complimentary trial account or log into your current account.
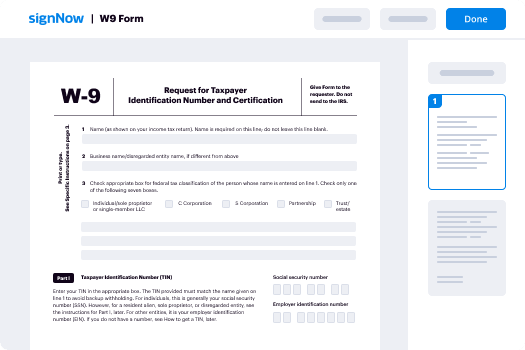
- Upload the document that requires your signature or that you want to distribute for signatures.
- If you intend to frequently use this document, think about saving it as a template.
- Open your document and make any necessary modifications, such as adding fillable fields or inserting specific details.
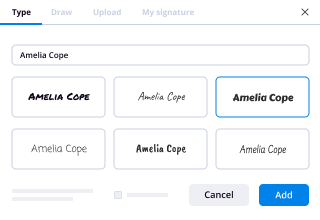
- Insert your signature and designate signature fields for other signers.
- Click 'Continue' to set up and send out an eSignature invitation.
By leveraging airSlate SignNow, organizations can optimize their document signing processes, realizing considerable savings and improved efficiency. The extensive feature set of this platform provides an excellent return on investment while ensuring that every document remains secure and compliant.
Eager to improve your document signing experience? Begin your free trial with airSlate SignNow today and uncover the benefits of signature validation for yourself!
How it works
Rate your experience
-
Best ROI. Our customers achieve an average 7x ROI within the first six months.
-
Scales with your use cases. From SMBs to mid-market, airSlate SignNow delivers results for businesses of all sizes.
-
Intuitive UI and API. Sign and send documents from your apps in minutes.
A smarter way to work: —how to industry sign banking integrate
FAQs
-
What is signature verification in airSlate SignNow?
Signature verification in airSlate SignNow ensures the authenticity of electronic signatures. This process confirms that the signature on a document is legitimate and has not been altered, providing businesses with peace of mind and legal assurance.
-
How does airSlate SignNow handle signature verification?
airSlate SignNow uses advanced encryption and authentication methods for signature verification. Each signed document has a unique digital certificate, allowing users to verify the identity of the signer and the integrity of the signature.
-
Is signature verification included in the airSlate SignNow pricing plans?
Yes, signature verification is included in all airSlate SignNow pricing plans. Our cost-effective solution provides businesses with essential features like signature verification without any hidden fees, making it accessible for all users.
-
Can I integrate signature verification with other tools?
Absolutely! airSlate SignNow offers seamless integrations with various applications, allowing you to incorporate signature verification into your existing workflows. This enhances productivity and ensures that your documents maintain their integrity across platforms.
-
What are the benefits of using airSlate SignNow for signature verification?
Using airSlate SignNow for signature verification enhances document security and compliance. It not only streamlines the signing process but also provides a reliable way to validate signatures, helping businesses avoid potential disputes.
-
How quickly can I verify a signature using airSlate SignNow?
Signature verification in airSlate SignNow is instant. Once a document is signed, users can quickly access the verification details, ensuring that you can confirm the signature's authenticity without delay.
-
Are there any limits on the number of signature verifications I can perform?
No, airSlate SignNow does not impose limits on the number of signature verifications you can perform. Our flexible plans allow you to verify as many signatures as necessary, ensuring your business operates smoothly.
-
Do agreements signed online by EchoSign or signNow have the same legal position as signed by hand?
Online signature software such as EchoSign or signNow use electronic signatures, also known as digital signatures.Most countries now have legislation that provide for the use of electronic signatures.However, these countries may have slightly different requirements for what constitutes a legally binding electronic signature.The United Nations has attempted to provide some unifying features through the UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Signatures 2001 but this model law has only been adopted in 32 states including the UK, China, Mexico and India.In the UK, the Electronic Communications Act 2000 was enacted to comply with the UNCITRAL Model Law but it has now been replaced by Europe’s Electronic Identification and Authentication Services Regulation (910/2014/EC)(eIDAS) which came into force on July 1 2016.This new law applies to all EU member states, but since BREXIT, it is uncertain whether the UK will continue with eIDAS.The eIDAS states that only "qualified electronic signatures" will be mutually accepted by all the EU member states. A qualified electronic signature must be uniquely linked to the signer and based on a qualified electronic certificate that is issued by an approved authority.In the USA, the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN, 2000) and the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA, 1999) give similar recognition to online signatures as paper signatures.Under these two acts, the term "electronic signature" means an electronic sound, symbol, or process, attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.Briefly, the following requirements must be met for an electronic signature to be valid:The signer intended to sign, consented to the use of electronic records for the transaction and did not withdraw his or her consent.The electronic transaction system must keep a record of how the signature was created or make a textual or graphic statement that must be attached to the agreement.The signer must have received a copy of the UETA consumer consent disclosures.The electronic signature records must be capable of being retained and accurately reproduced later by all parties. In other words, all parties must be allowed to reprint the agreement and the signatures if they want to.In Canada, electronic signatures are governed by the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA, 2000). A secure electronic signature must be:Unique to the person signing.The person signing has sole control over the signing process and his or her identify can be verified.The electronic signature is linked to an electronic document in a way that any attempt to change the document can be determined.In general, there's a lot of similarity in requirements governing electronic signatures, mainly because this is necessary to promote the growth of international e-commerce and trading.However, to avoid uncertainty, you should always state in your agreement which country’s law applies to the agreement. If there was going to be a dispute later on, you then know which country’s law will apply to the agreement and what the likely result will be.Also, even though you sign an agreement online using these software, ensure that you print a copy of the agreement and the signatures and keep these paper copies for your own records.For more info, you can check out our article on 4 tools to sign NDA agreements electronically.Credits: Icon "edit" by Chameleon Design from the Noun Project.
-
What is the difference between digital migration and digital signature?
The world that we are living in today is turning modern and more tech-savvy with each passing day. There are a lot of business options coming into the picture every day and the processes of making these businesses work are getting easier and smoother. One such important process that changes how businesses work today is the use of a digital signature or electronic signature.While both these terms are often used in place of each other, they hold different meanings attached to them. The use of a digital signature often occurs at times when you need to secure documents that are provided by certification authorities. On the other hand, an electronic signature is associated with contracts where two parties are collaborating in one way or the other.One of the unique features that characterize a digital signature is that is it is similar to a fingerprint embedded in a document which is to be sent digitally. The person who intends to sign this document needs to have a digital certificate which will allow them to link their identity to the document. A digital signature software allows you to generate digital signatures for yourself.The authorization of digital signatures is often carried out by certification authorities that provide digital certificates that can be checked with important documents like licenses and passports. There are many digital signature service providers also out there like eSignly that provide you with authentic digital signature for your important documents. A digital signature is strongly linked with the personality of a person.While that’s all about the digital signature, an electronic signature can be understood as an electronic symbol or process that is linked to a contract where both the involved parties are intended to sign the documents. An electronic signature can not only be in written form but it can be verbal as well.The best advantage of using a electronic signature via an esignature app is that is can be used by anyone, anywhere and at any time. They have no restrictions attached to them. So whether you a businessman or a freelancer, an electronic signature can always make things work for you.
-
Can NDAs (non-disclosure agreements) be signed through an online form? Are there any legal implications with an online form?
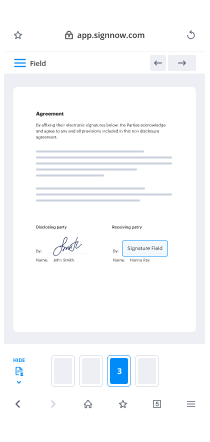
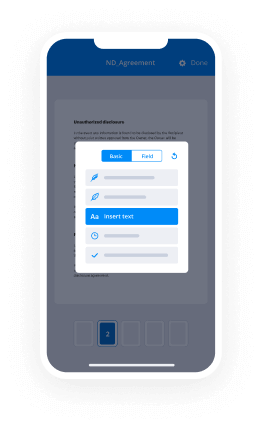
In a word: Yep!Thanks to the E-SIGN Act, documents signed electronically have the same legal protections as those signed with a physical pen! As long as your eSignature solution is committed to strong legality and your NDA is drafted by a professional, you absolutely can trust NDAs that are created, signed, and stored online.There are a few options out there. The rest of these examples are using signNow’s service. You can even create one now with a free signNow account.Here’s how to set up the NDA:Step 1: Acquire an NDA TemplateYou can find NDA templates online, but I would recommend seeking out a legal professional to create one that’s right for your needs.Step 2. Upload the Template, Add SignersAfter signing in to your signNow account, you’ll see the "Who needs to sign?" menu. For a confidentiality agreement, you’ll probably want to choose between “Me & others” or “Just others.” After selecting one, you’ll be able to drag and drop, choose “Add File,” or use any of our integrations to upload your non-disclosure agreement.Now you can add signers, loop in other parties via our CC feature, and assign a signer order if needed. Select “Prepare doc for signing” to move on to the really cool part!Step 3. Format the NDA and Fill in Your InformationWith the NDA you imported pulled up in front of you, click any of the fields across the top of the page and drag it to where you want to place it in the document. Most of the fields have advanced features and some even let you add a validation type (email address, numbers only, etc.) to help guide signers and reduce errors. Take some time to click around to get your NDA dialed in.Once you get your formatting just right, hit Continue at the top of the page. Back on the “Get your document signed” page, you’ll add a title, an optional message, and send your online NDA out for signatures!Step 4. Sign Your NDA Online (Legally and Securely!)If you’re one of the signers, a prompt to sign the non-disclosure agreement will hit your (and other signers’) email inbox as soon as you send it out for signatures. Just click the “Review & Sign” button in the email to continue.We provide a variety of ways to create your electronic signature:Draw your signature on a touch screen using your finger or a stylusUpload a photo of your signatureType in your signature and customize from a selection of fontTake a picture of your signature using your smartphone’s camerasignNow will automatically prompt each signer to complete all their required fields. Once you’ve filled out your portion of the NDA, all you have to do is agree to one last legality measure and your job is done!Step 5. Access Your Online NDA Any TimeTo check the status, edit, or even download a hard copy of your confidentiality agreement; just visit the Documents section of your signNow dashboard any time.
-
What are the biggest problems with digital or e-signatures?
[full disclosure: I’m VP Digital Transformation at Solutions Notarius Inc., a company that supplies electronic and digital signature solutions]Great question. I perceive the biggest challenges in relation to electronic and digital signatures to be:Not understanding the function of a signature and therefore what e-signatures are. In the physical world, people intuitively understand what a signature is in its manuscript form, whereas in the electronic world, e-signatures encompass a much wider range of possible forms, from email signature blocks to voice recordings to secured online session date (when you click « I accept ») to images of manuscript signatures to cryptographically protected digital signatures. A signature is a permanent mark that is unique, exclusively used and traceable to a person and affixed on static information with implied or expressed intention. Everything in the electronic world that fulfils that function is a signature.Not understanding that e-signatures are a means to an end / that end is legal reliability. Whenever you are applying a signature to something, especially documents, it is to create evidence of a transaction. The degree to which that evidence will possess the following four reliability attributes will affect the probative value of the evidence: identity (certainty of the identity of signers), integrity (certainty of no undetected changes to document / information signed), authenticity (all that is required to prove identity and longevity is embedded in the document itself) and longevity (document or information signed can be opened, read and authenticated for at least its retention period).Not understanding that there is no such thing as “universally legally valid e-signatures”. People often ask “are electronic signatures legal and are they recognized by courts”? Ascertaining the legality of a form of signature calls for a 4 step analysis, always. First, what is the applicable jurisdiction for a specific or category of information / documents? Some contracts for example include a forum conveniens clause which make applicable the laws of a specific jurisdiction. Second, in that jurisdiction, what are the form requirements for signing those documents? Form requirements may include signing before a Commissioner of oaths and some statutes even prescribe the use of paper (!) in some cases. Third, absent specific form requirements, what is the general default legal regime that governs e-signatures for that type of documents in that jurisdiction? Fourth, is the e-signature solution you plan to use / have used will meet statutory functional requirements? So, in conclusion and from the previous 4 step analysis, it should be clear there cannot possibly be any e-signature solution that is universally legally valid for all types of documents in all jurisdictions.Administrative Adoption. When UNCITRAL e-commerce model laws where adopted worldwide in the period 1998–2008, it created a vexing situation where e-signatures were legal but not administratively adopted. Even if a statute proclaims as a general rule, for example, that “you cannot deprive of legal effect a document that is electronically signed solely on the basis that it is electronic”, administrations such as governments and banks, when they insist on receiving and processing paper documents, are maintaining a barrier to the adoption of e-signatures that e-commerce statutes were supposed to help take down.Not understanding that e-signatures are not all equal when assessing reliability. To assess the reliability of a particular e-signature, one has to assess identity (is the identity of signers reliable? why?), integrity (are changes to the document correctly invaluable dating associated e-signatures? can the original document signed be retrieved notwithstanding changes?), authenticity (is all necessary information to prove identity and integrity embedded in the document - in which case the document is a proof; or not - in which case it is merely a commencement of proof) and longevity (is the document signed and preserved in a logical format - for example ISO 19005 PDF/A with PAdES LTV signatures) - that will ensure it remains readable and verifiable for as long as required?). The word of e-signatures, when it comes to understanding the range of reliability offered - or lack thereof! - is severally lacking in its general knowledge of what makes an e-signature reliable. For example, an signNow Self-Sign certificate that is auto-generated by a user is great for integrity but worthless for identity because the user can declare whatever identity they choose in the certificate.There are other problems and challenges of course but the above are top of mind challenges I see and encounter all the time.
-
What are the regulations for online beer sales in the UK?
Selling online: an overview of the rulesThis is an edited version of a guide for businesses.E-commerce TMT & Sourcing TMT Retail Education UKThere has been a steady growth in the variety and volume of goods and services which are available on-line to both businesses and consumers, and on-line selling is increasingly seen as a major way for all businesses to save costs. Almost inevitably, as the practice of on-line selling proliferates so does the amount of legislation governing it. This article provides an overview of the law governing on-line sales in the UK and an analysis of the issues that a business should consider before setting up an on-line sales process.The law governing online salesThere are two distinct types of legislation that affect on-line retailers. Firstly, traditional consumer protection regulations apply to all consumer sales made on-line. These regulations are well established, but it is important to remember that they apply to on-line retailers as much as they do to traditional ones. Secondly, there are regulations designed specifically to deal with problems and issues facing retailers on-line.Traditional consumer protection regulationsThese protect purchasers and consumers whether they are buying the goods over the counter of a shop or over the internet. For instance the Sale of Goods Act gives certain rights to purchasers about the quality of the goods they receive, and their rights if the goods fail to live up to these standards. The Consumer Credit Act protects consumers' rights when they enter into an agreement for someone to provide them with loans or credit facilities including circumstances where they buy goods or services using a credit card. The Unfair Terms in Consumer Contract Regulations protect consumers' rights where they enter into agreements with retailers who try to impose unfair terms in the agreement. There are also numerous other pieces of legislation, many of which will apply to different contract and product types.Online regulationsThese regulations are new, and were brought into force largely to protect consumers' rights when they buy products either over the internet or by telephone. They largely derive from EU Directives, and include the E-commerce Regulations , the Distance Selling Regulations and the Electronic Signatures Regulations . These are the regulations that control the actual on-line sales process and they provide the starting block from which we can consider the practical business requirements of on-line retailers.Although the traditional consumer regulations are important for all sales processes, this article focuses on the on-line regulations and how they affect the various stages of the on-line sales process. The next five sections take you through what the regulations require including information that must be provided to a purchaser, the use of electronic signatures, contract formation issues and ensuring your contract is legal.Information that must be suppliedThe various regulations share a central theme: companies should not hide themselves from purchasers, and should provide as much information to purchasers as possible.Company information that must be supplied under the E-Commerce RegulationsThe E-Commerce Regulations require that all commercial web sites make the following information directly and permanently available to consumers via the website:the company's name, postal address (and registered office address if this is different) and email address;the company's registration number;any Trade or Professional Association memberships;the company's VAT number.All of this applies regardlessof whether the site sells on-line. In addition, any commercial communication – that is any email or even SMS text message – used in providing an "Information Society Service" must display this information.The E-Commerce Regulations also require that all prices must be clear and unambiguous, and web sites must state whether the prices are inclusive of taxes and delivery costs.Contractual information that must be supplied under the E-Commerce RegulationsWhen it comes to actually going through the contractual process the requirements for information increase once again and the consumers must be told:the steps involved in completing the contract on-line;whether the contract will be stored by the retailer and/or permanently accessible;the technical means the site uses to allow consumers to spot and correct errors made while inputting their details prior to the order being placed;the languages offered to conclude the contract;The website must also provide links to any relevant Codes of Conduct to which the retailer subscribes and set out the retailer's Terms and Conditions, in a way which allows users to save and print them.All of this information must be provided before the purchaser selects the product and starts the contractual process and it is possible to convey it early on in the sale, without deterring users with an unwieldy sales process. The most common route is to bundle as many of these details into the terms and conditions as possible, and ensure that consumers are appropriately directed to read them.Information that must be supplied under the Distance Selling RegulationsThese Regulations set out the information which must be provided to a consumer prior to the conclusion of the contract.The information must be provided in a clear and comprehensible manner which is appropriate to the means of distance communication used. This means that the information can be set out on a web page, provided that the information is brought to the attention of the consumers before the contract is entered into. The information to be provided includes all of the information which a supplier should, in any event, wish to provide in relation to:the identity of the supplier;the main characteristics of the goods or services;their price;arrangements for payment and delivery; andthe existence of the right of cancellation created under the Distance Selling Regulations.Information that should be set out in the terms and conditionsThe terms and conditions should:make it clear who is selling the product, together with the geographical and email address;describe clearly what the customer is getting and what it will cost, including all taxes and delivery costs; andidentify the arrangements for delivery of the product.The terms and conditions of the site are very important, and will vary for every retailer. It is important that the terms and conditions are properly drafted, as poorly drafted terms and conditions will expose the retailer to unnecessary risk.Electronic signaturesThe Electronic Signature Regulations apply to any contract and not just those entered into with consumers. In order for there to be a binding contract the following essential elements of a contract must be present:an unconditional offer;an unconditional acceptance of that offer;consideration passing from both parties other than in Scotland where consideration is not a requirement; andan intention to create legal relations, i.e. the parties must intend to enter into a legally binding contract.There must also be certainty as to the terms, parties and subject matter of the contract. For the majority of contracts there is no legal requirement for a signature.Whenever a person buys or sells something he or she is entering into a contract, no matter how small the purchase. In the newsagents, when a person buys a newspaper he or she contracts with the newsagent for the purchase. The newsagent makes an 'Invitation to Treat' by placing the publication on sale. The person offers to purchase it from the newsagent, proffering money, and the offer is accepted (concluding the contract) by taking the money. This is still a contract, although not a word needs to be said, and nothing is written down. However, the essentials of a contract have been formed: an offer (to buy, or sell), an acceptance of that offer, and (everywhere except Scotland) consideration (whether money being paid, or some other form of consideration) for the sale. The various stages of the contractual process will be discussed in more detail later, as it is important to distinguish between who is making the offer and who is accepting it.Signatures are not actually necessary for the conclusion of every contract (your visit to the paper shop could become a chore), but they can have three essential functions when we consider on-line contracts:To identify the person who has bought the product;To indicate a personal involvement, or trustworthiness; andTo indicate an intention to be bound to the contract.The principal, and simple effect of the Electronic Signature Regulations is to make electronic signatures legally valid. Most of the discussion, and further interpretation of electronic signatures actually comes from a report published in December 2001 by the Law Commission entitled "Electronic Commerce: Formal requirements in Commercial Transactions", and in subsequent guidance from the DTI.Depending on exactly what is being sold the method of collecting the electronic signature will vary. In most cases, the function required of the electronic signature is the third one listed above – indicating that the purchaser is making an offer to contract. However, for more complex products being sold on-line, for instance financial services products, the role of the signature may become more important for one or both of the first two reasons.Depending on the value and/or importance of the transaction the parties may want a greater degree of certainty as to reliability of the signature. This may involve the use of public key infrastructure, for example.Contract formation issuesThe main issues considered in this section are how, when and where the contract is formed. This involves an analysis of the contract formation procedure based on the principle of offer and acceptance and the significance of the "country of origin" principle.The offer and acceptance procedure onlineStep 1: Establishing the offer and acceptance procedureThis is where the E-commerce Regulations can be used to the seller's advantage. It is possible to sell on-line and take payment by credit card without concluding the contract on-line. The solution is to provide that the customer is making an offer on the site and that the contract will be formed only if the customer's order is accepted – and that taking payment from the customer's credit card does not indicate cceptance.On-line merchant accounts provide for making refunds to a customer's credit card. Therefore, the terms should explain that, while the customer's card may be debited before the contract is formed, if the customer's order is ultimately rejected, a refund will be made immediately.Step 2: Completing the order formThe customer is taken to the order form where he completes the quantity of goods and his delivery details. It would be good practice to offer three buttons: submit, clear and cancel. The "clear" button is needed because the E-Commerce Regulations require a means for the customer to correct any errors.Step 3: Incorporating the terms and conditionsAt the bottom of the terms and conditions page the purchaser should, ideally, be required to check a box to indicate that he or she has read, understood and accepted the terms and conditions, before clicking the "Accept" button. The "Accept" button should not work until the box has been checked. Equally the page should be designed in such a way that the consumer cannot check the box and click "Accept" until the page has fully loaded onto the screen. By doing this, you improve your position in the event that a purchaser claims there was no opportunity to read your terms.While there is no responsibility on the retailer to ensure that the consumer has in fact read them, following this procedure will demonstrate that reasonable efforts have been made to bring them to purchasers' attention. The terms and conditions should be in a format that can be printed or saved – therefore avoid pop-up windows and ensure that they fit within the width of the page and are presented in a way that they will print properly.It is wise to also include a term like the following:"By clicking the 'Accept' button you agree to these terms and conditions. By completing and submitting the following electronic order form you are making an offer to purchase goods which, if accepted by us, will result in a binding contract."The words, "if accepted by us," are very important.This approach is the suggested 'best practice' approach for relaying the terms and conditions, and ensuring that the consumer has read them. However, it is not the most consumer friendly approach to present the purchaser with a screen of 'small print' in the middle of what, to the consumer, was an otherwise normal shopping experience. Therefore a number of on-line retailers adopt a second-best approach, which is to include a link to the terms and conditions, and make the consumer tick a box to confirm that they have read and accepted the terms and conditions, before they click the main button to buy the product. This approach, while not as legally secure, is probably acceptable in a number of purchasing models.Step 4: Taking the consumer's credit card details on-lineAt this stage, the user should be taken to the page on a secure server where his credit card details are taken. This page should state: "Your card will be debited with the sum of £X when you click the Submit button. This will be refunded if your offer is refused." Repeat the choice of submit, clear and cancel.Step 5: Acknowledging receipt of the orderWhen the card details are validated, the E-Commerce Regulations require that you give the customer an acknowledgement page and send an acknowledgement email. This should not confirm a contract; it should instead confirm that the order has been received and that the order is being "processed". It is helpful to give the customer an order number at this stage so that he or she can chase-up any problems. It is good practice, though not legally required, to ask the user to click a button on a confirmation page to indicate that he has read the confirmation – e.g. a "Continue" button, linking to the homepage of the site.Step 6: Providing confirmation of the information provided and the right to cancelThe Distance Selling Regulations now require the supplier to provide the consumer in writing or in another durable medium confirmation of the information provided prior to the conclusion of the contract and details of the right of cancellation. Generally a consumer has a period of seven working days within which to cancel the contract and return the goods to the supplier. The only cost to a consumer will be the cost of returning any goods received by it to the supplier.A consumer will not be entitled to cancel a contract after it has been entered into, where the supplier has commenced the provision of services with the consumer's agreement prior to the end of the cancellation period then the consumer will not have the right to cancel the contract for the provisional services. However, in order to benefit from this exception, the supplier must have advised the consumer that the consumer will not be able to cancel the contract once the performance of the services has begun with the consumer's agreement.It is not possible to contract out of the Distance Selling Regulations. Any term which attempts to do this will be void to the extent that it is inconsistent with the provisions of the distance Selling Regulations.Step 7: DeliveryFinally, dispatch the goods. If a typo mislabelled an item costing £200 at £2 and someone ordered 500 of them, the site could politely – and legally – refuse the order. This is because by following the procedure set out above the dispatch of goods is in effect the acceptance of the offer made by the consumer at the start of the process. Until this point there has been no acceptance and only an acknowledgement.The "country of origin" principleThe E-commerce Regulations apply a "country of origin" principle. In its simplest form, this means that as long as a UK business complies with UK laws, it can "ignore" the laws of other Member States. In general terms this is a definite bonus for on-line retailers. However, recognising that such an approach would be bad news for consumers, this basic rule is qualified.The E-Commerce Regulations do not apply the country of origin principle to the terms of consumer contracts. In practical terms, this means that a UK-based e-commerce site's terms and conditions should meet the laws of every Member State in which consumers can buy its products, not just UK laws.As a result of the consumer contract exception, any site selling to French consumers must provide its terms and conditions in French – otherwise they may be considered invalid. If selling into Denmark, consumers must be given a 14 working day cooling-off period during which the consumer can change his or her mind about the purchase and return the goods for a refund. In the UK, the cooling-off period is only seven working days. These are only examples, of course there are many other differences.Despite this signNow qualification, there are still advantages in the Regulations' country of origin principle that can benefit a UK-based business. For example, the UK's retail laws are among the most relaxed in Europe. This can give UK businesses advantages over, say, German competitors. A German e-tailer must comply with any German restrictions on promotional offers; its UK rival escapes such restrictions, even when selling to German consumers.Ensuring your contract is legalIt is important for e-commerce retailers to ensure that the contract which is formed with the consumer under the process described above is both legally correct and also affords the retailer the maximum protection. There are various ways in which the contracting process can be structured to be legally correct, and it is important to balance absolute best practice, and a more commercial approach which is still legally correct. Equally, it is surprisingly easy to structure the process in a way which is legally incorrect, and which exposes the company to more risk than is necessary.
-
Why should we validate a digital signature in e-Aadhaar while downloading? What are the uses for validating the digital signatur
A digital signature is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit. Digital signatures are commonly used for software distribution, financial transactions, and in some cases to detect forgery and tampering. Digital signatures employ asymmetric type of cryptography. For messages sent through an insecure channel, a properly implemented digital signature gives the receiver reason to believe the message was sent by the claimed sender. You may want to validate the signatures in e-Aadhaar while downloading to verify the signer and the signed content.Generally digital signatures are validated in order to achieve: Data integrity- Electronic signatures provides the confidence that the message has not been altered during transmission. Any change in the message after signature will invalidate the signature.Authentication- Electronic signatures are used to authenticate the source of messages. A valid signature shows that the message was sent by a specific user.Non-repudiation- Means that the signer cannot successfully claim they did not sign a message, while also claiming their private key remained secret. Some schemes provide a time stamp for electronic signatures.Understanding Cryptography
-
What will be the upcoming growth in the digital signature market?
The Digital Signature Market Research Report provides value chain analysis on the revenue for the forecast period 2016-2023 and estimates for each application in terms of market size, share, trend and growth. Furthermore, the report quantifies the market share held by the major players of the industry and provides an in-depth view of the competitive landscape. This market is classified into different segments with detailed analysis of each with respect to geography for the study period.The market size in terms of revenue (USD MN) is calculated for the study period along with the details of ...
Trusted esignature solution— what our customers are saying
Get legally-binding signatures now!
Frequently asked questions
How do i add an electronic signature to a word document?
How to sign a pdf in paint?
How to sign and seal pdf?
Get more for Validate Electronic signature Word Secure
- Can I Electronic signature Michigan General Power of Attorney Template
- Can I Electronic signature Minnesota General Power of Attorney Template
- How Do I Electronic signature California Distributor Agreement Template
- eSignature Michigan Escrow Agreement Simple
- How Do I Electronic signature Alabama Non-Compete Agreement
- How To eSignature North Carolina Sales Receipt Template
- Can I Electronic signature Arizona LLC Operating Agreement
- Electronic signature Louisiana LLC Operating Agreement Myself
Find out other Validate Electronic signature Word Secure
- Picture of beauty salon licence form
- City of southaven form
- Southaven building department form
- Horry county business license department post office form
- American credit acceptance funding checklist form
- Credit restoration agreement credit repair form
- Direct deposit change spire credit union form
- Alabama governor invokes god in banning nearly all abortions form
- Valet parking services agreement form
- Commonwealth of massachusetts affiliation notice mass form
- Commonwealth of massachusetts affiliation notice mass gov form
- State of alabama unified judicial system 5482933 form
- Mpc 630 mass gov mass form
- Community pharmacy medication safety incident pha form
- Affidavit of residency form for school
- Waterproofing certificate of compliance form
- A tax exempt 501c3 organization form
- Exosomes for hair restoration aftercare consent form
- Horse show entry form ircha
- Abi form